Principles that govern competition or co-existence in Rho-GTPase driven polarization
- PMID: 29649212
- PMCID: PMC5916526
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006095
Principles that govern competition or co-existence in Rho-GTPase driven polarization
Abstract
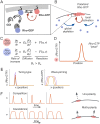
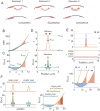
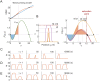
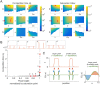
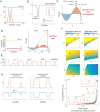
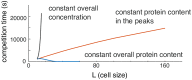
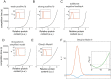
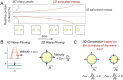
Rho-GTPases are master regulators of polarity establishment and cell morphology. Positive feedback enables concentration of Rho-GTPases into clusters at the cell cortex, from where they regulate the cytoskeleton. Different cell types reproducibly generate either one (e.g. the front of a migrating cell) or several clusters (e.g. the multiple dendrites of a neuron), but the mechanistic basis for unipolar or multipolar outcomes is unclear. The design principles of Rho-GTPase circuits are captured by two-component reaction-diffusion models based on conserved aspects of Rho-GTPase biochemistry. Some such models display rapid winner-takes-all competition between clusters, yielding a unipolar outcome. Other models allow prolonged co-existence of clusters. We investigate the behavior of a simple class of models and show that while the timescale of competition varies enormously depending on model parameters, a single factor explains a large majority of this variation. The dominant factor concerns the degree to which the maximal active GTPase concentration in a cluster approaches a "saturation point" determined by model parameters. We suggest that both saturation and the effect of saturation on competition reflect fundamental properties of the Rho-GTPase polarity machinery, regardless of the specific feedback mechanism, which predict whether the system will generate unipolar or multipolar outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Caceres A, Ye B, Dotti CG. Neuronal polarity: demarcation, growth and commitment. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2012;24(4):547–53. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2012.05.011 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature. 2002;420(6916):629–35. doi: 10.1038/nature01148 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yang Z. Cell polarity signaling in Arabidopsis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2008;24:551–75. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.23.090506.123233 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dotti CG, Sullivan CA, Banker GA. The establishment of polarity by hippocampal neurons in culture. J Neurosci. 1988;8(4):1454–68. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-04-01454.1988 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wu CF, Lew DJ. Beyond symmetry-breaking: competition and negative feedback in GTPase regulation. Trends Cell Biol. 2013;23(10):476–83. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2013.05.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

