Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis express a complex pro-inflammatory, pro-repair, angiogenic activation pattern, likely associated with macrophage iron accumulation
- PMID: 29649237
- PMCID: PMC5896901
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194803
Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis express a complex pro-inflammatory, pro-repair, angiogenic activation pattern, likely associated with macrophage iron accumulation
Erratum in
-
Correction: Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis express a complex pro-inflammatory, pro-repair, angiogenic activation pattern, likely associated with macrophage iron accumulation.PLoS One. 2018 May 17;13(5):e0197794. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197794. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29772026 Free PMC article.
Abstract
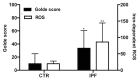
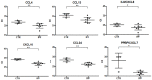
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a chronic lung disease of unknown cause characterized by alveolar epithelial damage, patchy interstitial fibrosis and diffuse microvascular abnormalities. In IPF, alveolar clustering of iron-laden alveolar macrophages-a common sign of microhemorrhage, has been associated with vascular abnormalities and worsening of pulmonary hypertension. As iron-dependent ROS generation has been shown to induce unrestrained macrophage activation in disease models of vascular damage, we explored alveolar macrophage activation phenotype in IPF patients (n = 16) and healthy controls (CTR, n = 7) by RNA sequencing of bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cells. The frequencies of macrophages in BAL cells were 86+4% and 83.4+8% in IPF and CTR groups, respectively (p-value = 0.41). In IPF patients, BAL cells showed increased iron-dependent ROS generation (p-value<0.05 vs CTR). Gene expression analysis showed overrepresentation of Gene Ontology processes/functions and KEGG pathways enriched in upregulated M1-type inflammatory (p-value<0.01), M2-type anti-inflammatory/tissue remodeling (p-value<0.0001), and MTPP-type chronic inflammatory/angiogenic (p-value<0.0001) chemokine and cytokine genes. The ex vivo finding was confirmed by the induction of iron-dependent ROS generation and chemokine/cytokine overexpression of Ccl4, Cxcl10 (M1), Il1rn (M2), Cxcl2, and Cxcl7 (MTPP) in MH-S murine immortalized alveolar macrophages exposed to ferric ammonium citrate in culture (p-value<0.05 vs CTR). The data show alveolar macrophage expression of a pro-inflammatory, tissue remodeling and angiogenic complex activation pattern, suggesting that iron accumulation may play a role in macrophage activation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, et al. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183(6):788–824. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2009-040GL . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bringardner BD, Baran CP, Eubank TD, Marsh CB. The role of inflammation in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2008;10(2):287–301. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1897 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schupp JC, Binder H, Jager B, Cillis G, Zissel G, Muller-Quernheim J, et al. Macrophage activation in acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116775 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0116775 . - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Foster MW, Morrison LD, Todd JL, Snyder LD, Thompson JW, Soderblom EJ, et al. Quantitative proteomics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Proteome Res. 2015;14(2):1238–49. doi: 10.1021/pr501149m . - DOI - PubMed
-
- Capelli A, Di Stefano A, Gnemmi I, Donner CF. CCR5 expression and CC chemokine levels in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2005;25(4):701–7. doi: 10.1183/09031936.05.00082604 . - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

