Confined placental mosaicism revisited: Impact on pregnancy characteristics and outcome
- PMID: 29649318
- PMCID: PMC5897023
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195905
Confined placental mosaicism revisited: Impact on pregnancy characteristics and outcome
Abstract
Objectives: We wanted to re-evaluate the influence of confined placental mosaicism subtypes (type 2 and type 3) on pregnancy characteristics and outcome.
Material and methods: From July 2009 to December 2015, 5512 chorionic villus samplings were performed in our Fetal Medicine Center. Conventional karyotyping was performed after long-term and short-term cultured villi to define type 2 or type 3 confined placental mosaicisms. Karyotype after amniocentesis was performed to exclude true fetal mosaicism, when appropriate. Pregnancy characteristics and outcomes were collected and compared to a control population.
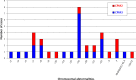
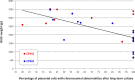
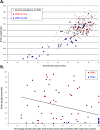
Results: Thirty-six (0.65%) confined placental mosaicisms were observed (13 type 2 and 23 type 3). Nuchal translucency was not increased for type 2 and type 3 confined placental mosaicisms. Pregnancy characteristics and outcomes were comparable between type 2 confined placental mosaicisms and the control population. In type 3 confined placental mosaicisms, median first trimester serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A was lower than for the control population (p<0.001), preterm births were noticed in 56% (p<0.001), small for gestational age newborns in 74% (p<0.001), and adverse pregnancy outcome was reported in 35% (p<0.01).
Conclusion: Although type 2 confined placental mosaicisms appeared to have no influence on pregnancy characteristics and outcome, type 3 confined placental mosaicisms were associated with low levels of first trimester serum pregnancy-associated plasma protein A, preterm birth, small for gestational age newborns, and adverse pregnancy outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Hahnemann JM, Vejerslev LO. European collaborative research on mosaicism in CVS (EUCROMIC)—fetal and extrafetal cell lineages in 192 gestations with CVS mosaicism involving single autosomal trisomy. Am J Med Genet. 1997;70:179–87. - PubMed
-
- Simoni G, Brambati B, Maggi F, Jackson L. Trisomy 16 confined to chorionic villi and unfavourable outcome of pregnancy. Ann Genet. 1992;35:110–2. - PubMed
-
- Roland B, Lynch L, Berkowitz G, Zinberg R. Confined placental mosaicism in CVS and pregnancy outcome. Prenat Diagn. 1994;14:589–93. - PubMed
-
- Goldberg JD, Wohlferd MM. Incidence and outcome of chromosomal mosaicism found at the time of chorionic villus sampling. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1997;176:1349–52. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

