Molecular characterization of the lipophorin receptor in the crustacean ectoparasite Lepeophtheirus salmonis
- PMID: 29649335
- PMCID: PMC5897026
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195783
Molecular characterization of the lipophorin receptor in the crustacean ectoparasite Lepeophtheirus salmonis
Abstract
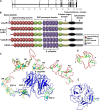
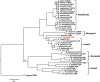
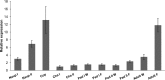
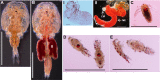
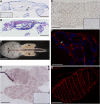
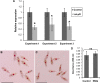
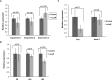
The Salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) is a marine ectoparasite of salmonid fish in the Northern Hemisphere and considered as a major challenge in aquaculture and a threat to wild populations of salmonids. Adult female lice produce a large number of lipid-rich eggs, however, the mechanism of maternal lipid transport into developing eggs during salmon louse reproduction has not been described. In the present study, a full-length L. salmonis lipophorin receptor (LsLpR) consisting of 16 exons was obtained by RACE and RT-PCR. The predicted ORF was 952 amino acids and structural analysis showed five functional domains that are similar to LpR of insects and decapods. Phylogenetic analysis placed the LsLpR together with LpRs from decapods and insects. Expression analysis revealed that the relative abundance of LsLpR transcripts was highest in the larvae and adult female lice. In adult females, the LsLpR transcripts and protein were found in the ovary and vitellogenic oocytes whereas, in larvae, the LsLpR transcripts were found in the neuronal somata of the brain and the intestine. Oil Red O stain results revealed that storage of neutral lipids was found in vitellogenic oocytes and ovaries of adult females, and in the yolk of larvae. Moreover, RNA interference (RNAi) was conducted to demonstrate the function of LsLpR in reproduction and lipid metabolism in L. salmonis. In larvae, the transcription of LsLpR was decreased by 44-54% while in an experiment LsLpR knockdown female lice produced 72% less offspring than control lice.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Westcott JD, Hammell KL, Burka JF. Sea lice treatments, management practices and sea lice sampling methods on Atlantic salmon farms in the Bay of Fundy, New Brunswick, Canada. Aquac Res. 2004;35(8):784–92. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2109.2004.01101.x WOS:000222291100010. - DOI
-
- Costello MJ. How sea lice from salmon farms may cause wild salmonid declines in Europe and North America and be a threat to fishes elsewhere. P R Soc B. 2009;276(1672):3385–94. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2009.0771 WOS:000269241300001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hamre LA, Eichner C, Caipang CM, Dalvin ST, Bron JE, Nilsen F, et al. The Salmon Louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae) life cycle has only two Chalimus stages. PloS one. 2013;8(9):e73539 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073539 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3772071. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tucker CS SC, Wootten R. An investigation onto the larval energetics and settlement of sea louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, an ectoparasitic copepod of Atlantic salmon, Salmo salar. Fish Path. 2000;35(3):137–43.
-
- Dalvin S, Frost P, Biering E, Hamre LA, Eichner C, Krossoy B, et al. Functional characterisation of the maternal yolk-associated protein (LsYAP) utilising systemic RNA interference in the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) (Crustacea: Copepoda). Int J Parasitol. 2009;39(13):1407–15. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpara.2009.04.004 WOS:000270495800001. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

