Polymeric micelles: Theranostic co-delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs and contrast agents
- PMID: 29649747
- PMCID: PMC5918157
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.03.054
Polymeric micelles: Theranostic co-delivery system for poorly water-soluble drugs and contrast agents
Abstract
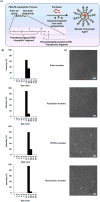
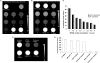
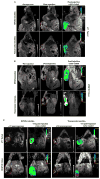
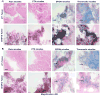
Interest in theranostic agents has continued to grow because of their promise for simultaneous cancer detection and therapy. A platform-based nanosized combination agent suitable for the enhanced diagnosis and treatment of cancer was prepared using polymeric polyethylene glycol-phosphatidylethanolamine-based micelles loaded with both, poorly soluble chemotherapeutic agent paclitaxel and hydrophobic superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPION), a Magnetic Resonance Imaging contrast agent. The co-loaded paclitaxel and SPION did not affect each other's functional properties in vitro. In vivo, the resulting paclitaxel-SPION-co-loaded PEG-PE micelles retained their Magnetic Resonance contrast properties and apoptotic activity in breast and melanoma tumor mouse models. Such theranostic systems are likely to play a significant role in the combined diagnosis and therapy that leads to a more personalized and effective form of treatment.
Keywords: Cancer therapy; Diagnostics; Drug delivery; Micelles; Nanoparticles; Theranostics.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- MacKay JA, Li Z. Theranostic agents that co-deliver therapeutic and imaging agents? Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010;62(11):1003–4. - PubMed
-
- Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y, Hori K. Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in macromolecular therapeutics: a review. J Control Release. 2000;65(1–2):271–84. - PubMed
-
- Hahn MA, Singh AK, Sharma P, Brown SC, Moudgil BM. Nanoparticles as contrast agents for in-vivo bioimaging: current status and future perspectives. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2011;399(1):3–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

