The dose distribution in dominant intraprostatic tumour lesions defined by multiparametric MRI and PSMA PET/CT correlates with the outcome in patients treated with primary radiation therapy for prostate cancer
- PMID: 29650029
- PMCID: PMC5898009
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-018-1014-1
The dose distribution in dominant intraprostatic tumour lesions defined by multiparametric MRI and PSMA PET/CT correlates with the outcome in patients treated with primary radiation therapy for prostate cancer
Abstract
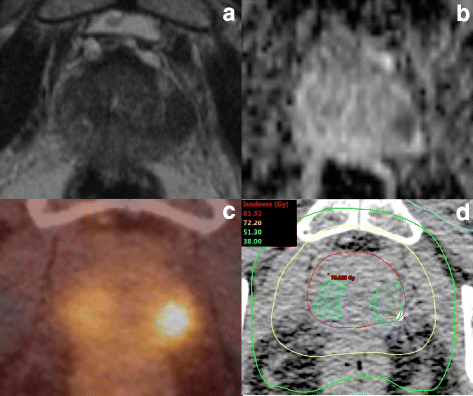
Background: We hypothesized that dominant intraprostatic lesions (DILs) could be depictured by multimodal imaging techniques (MRI and/or PSMA PET/CT) in patients with primary prostate cancer (PCa) and investigated possible effects of radiotherapy (RT) dose distribution within the DILs on the patients’ outcome.
Methods: One hundred thirty-eight patients with localized prostate cancer (PCa) and visible DIL underwent primary external beam RT between 2008 and 2016 with an aimed prescription dose of 76 Gy to the whole prostate. Seventy-five patients (54%) additionally received androgen deprivation therapy. Three volumes were retrospectively generated: DIL using pretreatment MRI and/or PSMA PET/CT, prostatic gland (PG) and the subtraction between PG and DIL (SPG). The minimum dose (Dmin), maximum dose (Dmax) and mean dose (Dmean) in the three respective volumes were calculated. Biochemical recurrence free survival (BRFS) was considered in uni- and multivariate Cox regression analyses. An explorative analysis was performed to determine cut-off values for the three dose parameters in the three respective volumes.
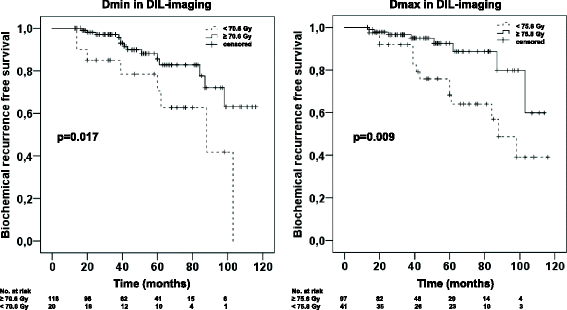
Results: With a median follow-up of 45 months (14–116 months) 15.9% of patients experienced BR. Dmin (cut-off: 70.6 Gy, HR = 0.39, p = 0.036) applied to the DIL had an impact on BRFS in multivariate analysis, in contrast to the Dmin delivered to PG and SPG which had no significant impact (p > 0.05). Dmin was significantly (p < 0.004) lower in patients with BR than in patients without BR. Dmax within DIL-imaging (cut-off: 75.8 Gy, HR = 0.31, p = 0.009) and in both PG und SPG (cut-off: 76 Gy, HR = 0.32, p = 0.009) had a significant impact on the BRFS. 95% of patients with a Dmax ≥76 Gy in SPG had a Dmin ≥70.6 Gy in DIL-imaging. Dmean in all of the three volumes had no significant impact on BRFS (p > 0.05).
Conclusions: The dose distribution within DILs defined by PSMA PET/CT and/or MRI is an independent risk factor for BR after primary RT in patients with PCa. These findings support the implementation of imaging based DIL interpretation for RT treatment planning, although further validation in larger patient cohorts with longer follow-up is needed.
Keywords: Dominant lesion; MRI; PSMA PET/CT; Prostate cancer; Radiation dose.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All patients gave written consent to undergo pretreatment imaging (MRI and/or PSMA PET/CT) and radiotherapy. This retrospective analysis is in compliance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and its subsequent amendments [28]. It was approved by the local Ethics Committee.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Pucar D, Hricak H, Shukla-Dave A, et al. Clinically significant prostate cancer local recurrence after radiation therapy occurs at the site of primary tumor: magnetic resonance imaging and step-section pathology evidence. Int J Radiat Oncol. 2007;69(1):62–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.03.065. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mendez LC, Ravi A, Chung H, et al. Pattern of relapse and dose received by the recurrent intraprostatic nodule in low- to intermediate-risk prostate cancer treated with single fraction 19 Gy high dose-rate brachytherapy. Brachytherapy. 2018;17(2):291-7. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

