The Vasculature in Prediabetes
- PMID: 29650631
- PMCID: PMC5901903
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.118.311912
The Vasculature in Prediabetes
Abstract
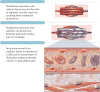
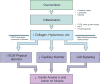
The frequency of prediabetes is increasing as the prevalence of obesity rises worldwide. In prediabetes, hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, and inflammation and metabolic derangements associated with concomitant obesity cause endothelial vasodilator and fibrinolytic dysfunction, leading to increased risk of cardiovascular and renal disease. Importantly, the microvasculature affects insulin sensitivity by affecting the delivery of insulin and glucose to skeletal muscle; thus, endothelial dysfunction and extracellular matrix remodeling promote the progression from prediabetes to diabetes mellitus. Weight loss is the mainstay of treatment in prediabetes, but therapies that improved endothelial function and vasodilation may not only prevent cardiovascular disease but also slow progression to diabetes mellitus.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; extracellular matrix; insulin resistance; metabolic syndrome; obesity.
© 2018 American Heart Association, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Menke A, Casagrande S, Geiss L, Cowie CC. Prevalence of and Trends in Diabetes Among Adults in the United States, 1988-2012. JAMA. 2015;314:1021–9. - PubMed
-
- Guariguata L, Whiting DR, Hambleton I, Beagley J, Linnenkamp U, Shaw JE. Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2013 and projections for 2035. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2014;103:137–49. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Definition and diagnosis of diabetes mellitus and intermediate hyperglycaemia. 2006 http://appswhoint/iris/bitstream/10665/43588/1/9241594934_engpdf.
-
- DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979;237:E214–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK108159/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK050277/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U2C DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK096527/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK054902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL125426/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007411/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL128983/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK050277/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK054902/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132320/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 DK059637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL102780/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

