Genetic and physiological basis for antibody production by Kluyveromyces marxianus
- PMID: 29651657
- PMCID: PMC5897269
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-018-0588-1
Genetic and physiological basis for antibody production by Kluyveromyces marxianus
Abstract
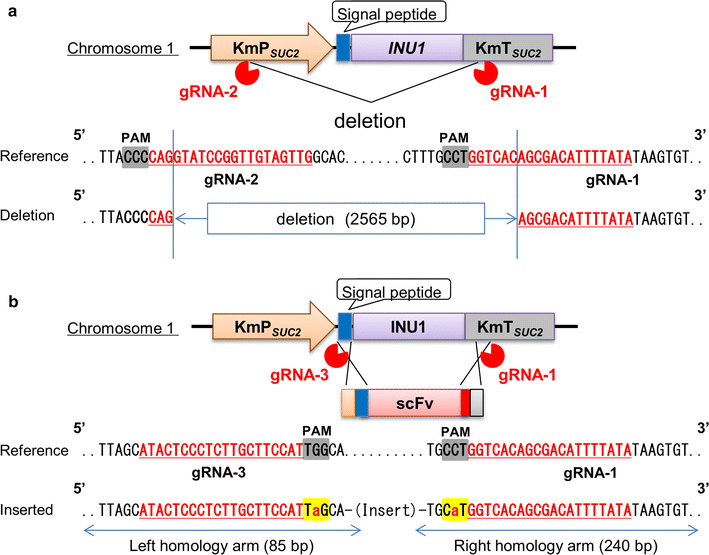
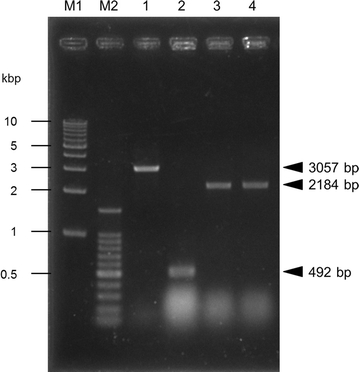
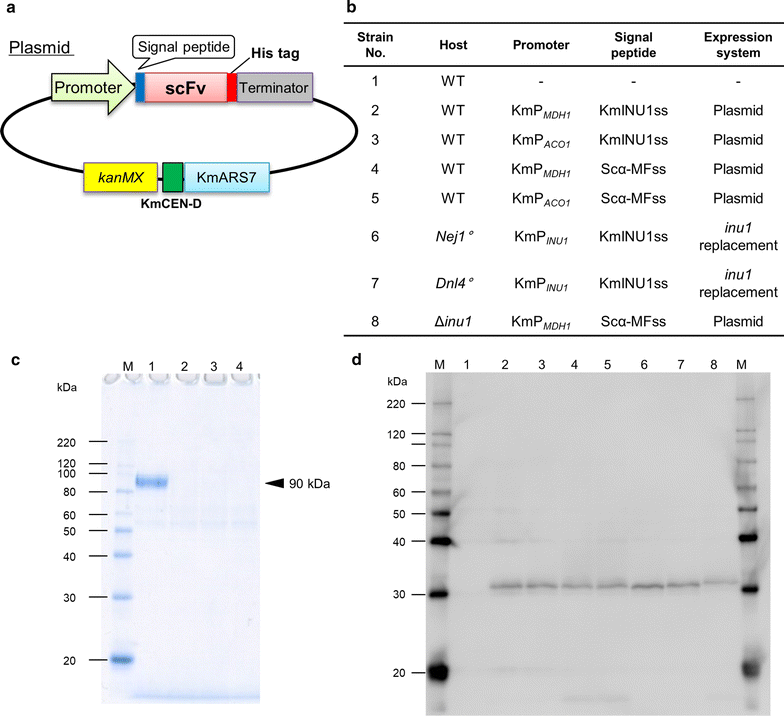
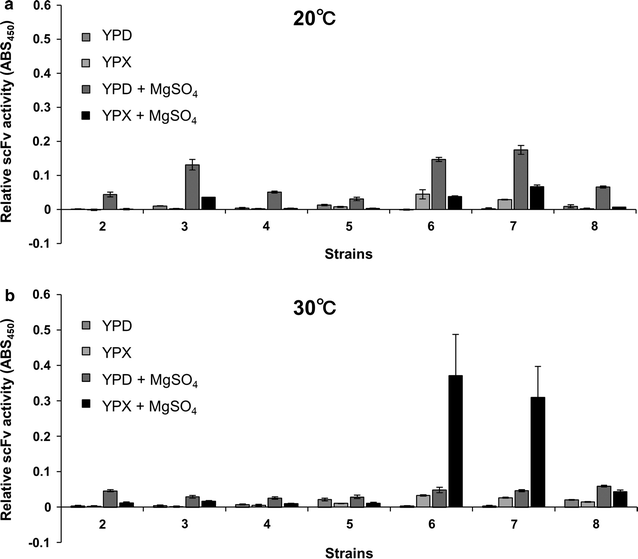
Kluyveromyces marxianus is a thermotolerant, crabtree-negative yeast, which preferentially directs metabolism (e.g., from the tricarboxylic acid cycle) to aerobic alcoholic fermentation. Thus K. marxianus has great potential for engineering to produce various materials under aerobic cultivation conditions. In this study, we engineered K. marxianus to produce and secrete a single-chain antibody (scFv), a product that is highly valuable but has historically proven difficult to generate at large scale. scFv production was obtained with strains carrying either plasmid-borne or genomically integrated constructs using various combinations of promoters (P MDH1 or P ACO1 ) and secretion signal peptides (KmINUss or Scα-MFss). As the wild-type K. marxianus secretes endogenous inulinase predominantly, the corresponding INU1 gene was disrupted using a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated protein (CRISPR-Cas9) system to re-direct resources to scFv production. Genomic integration was used to replace INU1 with sequences encoding a fusion of the INU1 signal peptide to scFv; the resulting construct yielded the highest scFv production among the strains tested. Optimization of growth conditions revealed that scFv production by this strain was enhanced by incubation at 30 °C in xylose medium containing 200 mM MgSO4. These results together demonstrate that K. marxianus has the potential to serve as a host strain for antibody production.
Keywords: INU1; Inulinase; Kluyveromyces marxianus; MgSO4; Single-chain antibody (scFv).
Figures
References
-
- Brachmann CB, Davies A, Cost GJ, Caputo E, Li J, Hieter P, Boeke JD. Designer deletion strains derived from Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C: a useful set of strains and plasmids for PCR-mediated gene disruption and other applications. Yeast. 1998;14(2):115–132. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0061(19980130)14:2<115::AID-YEA204>3.0.CO;2-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

