The Role and Mechanism of Borneol to Open the Blood-Brain Barrier
- PMID: 29652199
- PMCID: PMC6142104
- DOI: 10.1177/1534735418767553
The Role and Mechanism of Borneol to Open the Blood-Brain Barrier
Abstract
Background: The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is the greatest challenge in the treatment of intracranial malignant tumors.
Objective: The aim of this study is to determine the role of borneol in opening the BBB and elucidate the underlying mechanisms.
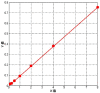
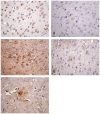
Materials and methods: Twenty Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were randomized into borneol group intragastrically administered with 10% borneol corn oil (2 mL/kg) and control group. After 30 minutes, 2% Evans blue (4 mL/kg) was injected. Thirty minutes later, brain tissue was analyzed using the Evans blue standard curve. Another 40 SD rats were randomized into high-, medium-, and low-dose borneol groups and a control group. Each rat in the experimental groups was intragastrically administered with 10% borneol corn oil (2 mL/kg, 1.25 mL/kg, and 0.5 mL/kg, respectively). The control group was injected with corn oil of 1.25 mL/kg. After 30 minutes, the rats were killed, and the brain tissues were collected. The expression of occludin, occludens-1, nitric oxide synthase, P-glycoprotein, and intercellular cell adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) was detected by immunohistochemy.
Results: The concentration of Evans blue in the borneol group was higher than in the control group ( P < .05). The mean density of ICAM-1 expression was higher in the experimental group than in the control group ( P < .05). In contrast, significant differences of positive area and total density of ICAM-1 were shown only between the high-dose group and the control group ( P < .05).
Conclusion: Borneol can open the BBB, which might be related with the increased expression of ICAM-1.
Keywords: ICAM-1; SD rats; blood-brain barrier; borneol; traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin DM. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 2010;127:2893-2917. - PubMed
-
- Alexandru D, Bota DA, Linskey ME. Epidemiology of central nervous system metastases. Prog Neurol Surg. 2012;25:13-29. - PubMed
-
- Bhatia SP, McGinty D, Letizia CS, Api AM. Fragrance material review on l-borneol. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008;46(suppl 11):S81-S84. - PubMed
-
- Zhang L, Han L, Qin J, Lu W, Wang J. The use of borneol as an enhancer for targeting aprotinin-conjugated PEG-PLGA nanoparticles to the brain. Pharm Res. 2013;30:2560-2572. - PubMed
-
- Xin HL, He XR, Li W, Zhou ZD, Zhang S, Wang GJ. The effect of borneol on the concentration of meropenem in rat brain and blood. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2014;16:648-657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

