Clathrin coat controls synaptic vesicle acidification by blocking vacuolar ATPase activity
- PMID: 29652249
- PMCID: PMC5935483
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.32569
Clathrin coat controls synaptic vesicle acidification by blocking vacuolar ATPase activity
Abstract
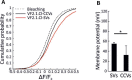
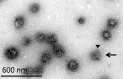
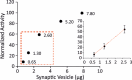
Newly-formed synaptic vesicles (SVs) are rapidly acidified by vacuolar adenosine triphosphatases (vATPases), generating a proton electrochemical gradient that drives neurotransmitter loading. Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is needed for the formation of new SVs, yet it is unclear when endocytosed vesicles acidify and refill at the synapse. Here, we isolated clathrin-coated vesicles (CCVs) from mouse brain to measure their acidification directly at the single vesicle level. We observed that the ATP-induced acidification of CCVs was strikingly reduced in comparison to SVs. Remarkably, when the coat was removed from CCVs, uncoated vesicles regained ATP-dependent acidification, demonstrating that CCVs contain the functional vATPase, yet its function is inhibited by the clathrin coat. Considering the known structures of the vATPase and clathrin coat, we propose a model in which the formation of the coat surrounds the vATPase and blocks its activity. Such inhibition is likely fundamental for the proper timing of SV refilling.
Keywords: E. coli; acidification; clathrin coat; endocytosis; human; mouse; neuroscience; proton pump; synaptic vesicle; vATPase.
© 2018, Farsi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ZF, SG, MK, BR, AW, EL, CM, IM No competing interests declared, RJ Reviewing editor, eLife
Figures

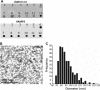
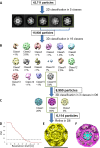
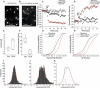

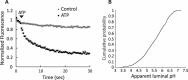


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

