Temperature Effects Explain Continental Scale Distribution of Cyanobacterial Toxins
Affiliations
- 1 Department F.-A. Forel for Environmental and Aquatic Sciences, University of Geneva, 1205 Geneva, Switzerland. Evanthia.Mantzouki@unige.ch.
- 2 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. miquel.lurling@wur.nl.
- 3 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. miquel.lurling@wur.nl.
- 4 German Environment Agency, Unit Drinking Water Resources and Water Treatment, Corrensplatz 1, 14195 Berlin, Germany. jutta.fastner@uba.de.
- 5 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.desenerpontdomis@nioo.knaw.nl.
- 6 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.desenerpontdomis@nioo.knaw.nl.
- 7 Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-120 Krakow, Poland. wilk@iop.krakow.pl.
- 8 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. judita.koreiviene@gmail.com
- 9 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.seelen@nioo.knaw.nl
- 10 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.seelen@nioo.knaw.nl
- 11 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. s.teurlincx@nioo.knaw.nl
- 12 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. yvonverstijnen@hotmail.com
- 13 Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-120 Krakow, Poland. krzton@iop.krakow.pl
- 14 Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-120 Krakow, Poland. walusiak@iop.krakow.pl
- 15 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. jurate.karosiene@botanika.lt
- 16 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. jurate.kasperoviciene@botanika.lt
- 17 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. ksenija.savadova@gamtostyrimai.lt
- 18 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. irma.vitonyte@gmail.com
- 19 R&D Department Environmental Engineering, 3edata, 27004 Lugo, Spain. carmen.cillero@3edata.es
- 20 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. ag.budzynska@gmail.com
- 21 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. rgold@amu.edu.pl
- 22 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. akozak@amu.edu.pl
- 23 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. rosinska.asia@gmail.com
- 24 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. eszelag@amu.edu.pl
- 25 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. domekp@amu.edu.pl
- 26 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. jakubowskan@gmail.com
- 27 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. kingakwasizur@wp.pl
- 28 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. messyasz@amu.edu.pl
- 29 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. ola.p@amu.edu.pl
- 30 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. marpel@amu.edu.pl
- 31 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. kok@amu.edu.pl
- 32 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. ana.garcia@aecom.com
- 33 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. montserrat.real@aecom.com
- 34 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. elvira.romans@aecom.com
- 35 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. jordi.noguero@aecom.com
- 36 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. parra1404@hotmail.com
- 37 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. elifdzmo@gmail.com
- 38 Department of Environmental Engineering, Abant Izzet Baysal University, 14280 Bolu, Turkey. karakaya_n@ibu.edu.tr
- 39 Department of Science and Engineering, Åbo Akademi University, 20520 Åbo, Finland. kerstin.haggqvist@gmail.com
- 40 Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture, Ankara University, 6100 Ankara, Turkey. nilsundemir2@gmail.com
- 41 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. meryem@metu.edu.tr
- 42 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. nrflzster@gmail.com
- 43 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. eti@thelevis.com
- 44 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. iskin.ugur@gmail.com
- 45 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. gizbezirci@gmail.com
- 46 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. unyazgan@gmail.com
- 47 Institute of Marine Sciences, Department of Oceanography, Middle East Technical University, 06800 Ankara, Turkey. koray@ims.metu.edu.tr
- 48 Department of Botany, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece. sgkelis@bio.auth.gr
- 49 Department of Botany, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece. mattpano@bio.auth.gr
- 50 Department of Basic Science, Ataturk University, 25240 Erzurum, Turkey. ozden.fakioglu@atauni.edu.tr
- 51 Water Quality Department, Athens Water Supply and Sewerage Company, 11146 Athens, Greece. c.avagianos@icloud.com
- 52 Water Quality Department, Athens Water Supply and Sewerage Company, 11146 Athens, Greece. t_kaloudis@ath.forthnet.gr
- 53 Department of Biology, Balikesir University, 10145 Balikesir, Turkey. kcelik@balikesir.edu.tr
- 54 Department of Bioengineering, Bursa Technical University, 16310 Bursa, Turkey. mete.yilmaz@btu.edu.tr
- 55 Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA), 17003 Girona, Spain. rmarce@icra.cat
- 56 Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA), 17003 Girona, Spain. ncatalangarcia@gmail.com
- 57 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. ncatalangarcia@gmail.com
- 58 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. jandriugarcia@gmail.com
- 59 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. moritz.buck@ebc.uu.se
- 60 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. william.colom@ebc.uu.se
- 61 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. kristiina.mustonen@ebc.uu.se
- 62 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. don.pierson@ebc.uu.se
- 63 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. yang.yang@hotmail.se
- 64 Research Center in Biodiversity and Genetic Resources (CIBIO-Azores), InBIO Associated Laboratory, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of the Azores, 9501-801 Ponta Delgada, Portugal. pedro.mv.raposeiro@uac.pt
- 65 Research Center in Biodiversity and Genetic Resources (CIBIO-Azores), InBIO Associated Laboratory, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of the Azores, 9501-801 Ponta Delgada, Portugal. vitor.mc.goncalves@uac.pt
- 66 Department of Environmental Science and Technology, Cyprus University of Technology, 3036 Lemesos, Cyprus. maria.antoniou@cut.ac.cy
- 67 Department of Environmental Science and Technology, Cyprus University of Technology, 3036 Lemesos, Cyprus. tsiarta.nikoletta@gmail.com
- 68 Centre for Freshwater and Environmental Studies, Dundalk Institute of Technology, A91 K584 Dundalk, Ireland. valerie.mccarthy@dkit.ie
- 69 Centre for Freshwater and Environmental Studies, Dundalk Institute of Technology, A91 K584 Dundalk, Ireland. victorc.perello@dkit.ie
- 70 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. tonu.feldmann@emu.ee
- 71 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. alo.laas@emu.ee
- 72 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. kristel.panksep@emu.ee
- 73 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. lea.tuvikene@emu.ee
- 74 European Regional Centre for Ecohydrology of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 90364 Lodz, Poland. ilonagagala@erce.unesco.lodz.pl
- 75 European Regional Centre for Ecohydrology of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 90364 Lodz, Poland. j.mankiewicz@erce.unesco.lodz.pl
- 76 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. meralyagci@gmail.com
- 77 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. sakircinar@gmail.com
- 78 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. kadircapkin32@hotmail.com
- 79 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. a.k.yagci58@gmail.com
- 80 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. mehmetcesur3232@gmail.com
- 81 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. fuatbilgin@gmail.com
- 82 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. caferbulut@gmail.com
- 83 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. uysalrahmi@hotmail.com
- 84 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. ulrike.obertegger@fmach.it
- 85 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. adriano.boscaini@fmach.it
- 86 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. giovanna.flaim@fmach.it
- 87 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. nico.salmaso@fmach.it
- 88 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. leonardo.cerasino@fmach.it
- 89 Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences, University of Stirling, Stirling FK9 4LA, UK. jerich15@ceh.ac.uk
- 90 Department of Freshwater and Marine Ecology, University of Amsterdam, 1090 GE Amsterdam, The Netherlands. p.m.visser@uva.nl
- 91 Department of Freshwater and Marine Ecology, University of Amsterdam, 1090 GE Amsterdam, The Netherlands. j.m.h.verspagen@uva.nl
- 92 Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Gaziosmanpasa University, 60250 Merkez, Turkey. biyo_tunay@hotmail.com
- 93 Department of Biology, Giresun University, 28100 Giresun, Turkey. elif.neyran.soylu@giresun.edu.tr
- 94 Department of Biology, Hitit University, 19040 Corum, Turkey. farukmaraslioglu@hitit.edu.tr
- 95 Department of Icthyology, Hydrobiology and Aquatic Ecology, Inland Fisheries Institute, 10719 Olsztyn, Poland. a.napiorkowska-krzebietke@infish.com.pl
- 96 Department of Freshwater Protection, Institute of Environmental Protection- National Research Institute, 01-692 Warsaw, Poland. a.ochocka@ios.edu.pl
- 97 Department of Freshwater Protection, Institute of Environmental Protection- National Research Institute, 01-692 Warsaw, Poland. paszta@ios.edu.pl
- 98 Centro de Investigação da Montanha, Instituto Politécnico de Bragança, Campus de Santa Apolónia, 5300-253 Bragança, Portugal; geraldes@ipb.pt
- 99 Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR) and University of Porto, 4450-208 Matosinhos, Portugal. vmvascon@fc.up.pt
- 100 Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR) and University of Porto, 4450-208 Matosinhos, Portugal. joaopmorais@gmail.com
- 101 Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR) and University of Porto, 4450-208 Matosinhos, Portugal. mica.ciimar@gmail.com
- 102 Department of Freshwater Resource and Management, Faculty of Aquatic Sciences, Istanbul University, 34134 Istanbul, Turkey. latifekoker@gmail.com
- 103 Department of Freshwater Resource and Management, Faculty of Aquatic Sciences, Istanbul University, 34134 Istanbul, Turkey. rakcaalan@gmail.com
- 104 Department of Freshwater Resource and Management, Faculty of Aquatic Sciences, Istanbul University, 34134 Istanbul, Turkey. albay.hermano@gmail.com
- 105 Department of Biology, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, 31000 Osijek, Croatia. dspoljaric@biologija.unios.hr
- 106 Department of Biology, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, 31000 Osijek, Croatia. fstevic@biologija.unios.hr
- 107 Department of Biology, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, 31000 Osijek, Croatia. tzuna@biologija.unios.hr
- 108 Department of Experimental Limnology, Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries, 16775 Stechlin, Germany. fonvielle@igb-berlin.de
- 109 Department of Biology, Limnological Institute, University of Konstanz, 78464 Konstanz, Germany. dietmar.straile@uni-konstanz.de
- 110 Department of Biology, Limnological Institute, University of Konstanz, 78464 Konstanz, Germany. karl.rothhaupt@uni-konstanz.de
- 111 Department of Biology, Lund University, 22362 Lund, Sweden. lars-anders.hansson@biol.lu.se
- 112 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. pablo.urrutia_cordero@biol.lu.se
- 113 Department of Biology, Lund University, 22362 Lund, Sweden. pablo.urrutia_cordero@biol.lu.se
- 114 RECETOX, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, 62500 Brno, Czech Republic. blaha@recetox.muni.cz
- 115 Department of Hydrobiology, Morava Board Authority, 60200 Brno, Czech Republic. geris@pmo.cz
- 116 Laboratory of Paleoecology, Institute of Botany, The Czech Academy of Sciences, 60200 Brno, Czech Republic. marketka.kozakova@seznam.cz
- 117 Department of Environment and Resource Management, Mediterranean Fisheries Research Production and Training Institute, 7090 Antalya, Turkey. matkocer@hotmail.com
- 118 Faculty of Aquaculture, Mersin University, 33160 Mersin, Turkey. talp@mersin.edu.tr
- 119 Department ofWater Quality, Slovenian Environmental Agency, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia. spela.remec-rekar@gov.si
- 120 Department of Genetic Toxicology and Cancer Biology, National Institute of Biology, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia. tina.elersek@nib.si
- 121 Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, National Center for Scientific Research «DEMOKRITOS», 15341 Attiki, Greece. t.triantis@inn.demokritos.gr
- 122 Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, National Center for Scientific Research «DEMOKRITOS», 15341 Attiki, Greece. s.zervou@inn.demokritos.gr
- 123 Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, National Center for Scientific Research «DEMOKRITOS», 15341 Attiki, Greece. a.hiskia@inn.demokritos.gr
- 124 Department of Freshwater Ecology, Norwegian Institute for Water Research, 0349 Oslo, Norway. sigrid.haande@niva.no
- 125 Department of Freshwater Ecology, Norwegian Institute for Water Research, 0349 Oslo, Norway. birger.skjelbred@niva.no
- 126 Institute of Environmental Engineering, Poznan University of Technology, 60965 Poznan, Poland. beata.madrecka@put.poznan.pl
- 127 National Reference Center for Hydrobiology, Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic, 82645 Bratislava, Slovakia. hana.nemova@uvzsr.sk
- 128 National Reference Center for Hydrobiology, Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic, 82645 Bratislava, Slovakia. iveta.drastichova@uvzsr.sk
- 129 National Reference Center for Hydrobiology, Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic, 82645 Bratislava, Slovakia. lucia.chomova@uvzsr.sk
- 130 School of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen AB10 7GJ, UK. c.edwards@rgu.ac.uk
- 131 Department of Biology, Sakarya University, 54187 Sakarya, Turkey. tsevindik@sakarya.edu.tr
- 132 Department of Biology, Sakarya University, 54187 Sakarya, Turkey. htunca@sakarya.edu.tr
- 133 Department of Biology, Sakarya University, 54187 Sakarya, Turkey. burcin.onem1@ogr.sakarya.edu.tr
- 134 Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, SS Cyril and Methodius University, 1000 Skopje, Macedonia. borisaleksovski@pmf.ukim.mk
- 135 Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, SS Cyril and Methodius University, 1000 Skopje, Macedonia. skrstic@pmf.ukim.mk
- 136 Department for Ecotoxicology, Teaching Institute of Public Health of Primorje-Gorski Kotar County, 51000 Rijeka, Croatia. itana.bokan@zzjzpgz.hr
- 137 Institute of Technology, The State University of Applied Sciences, 82300 Elblag, Poland. nawrocka.lidia@op.pl
- 138 Department of Biological and Environmental Science, University of Jyväskylä, 40014 Jyväskylä, Finland. pauliina.u.m.salmi@jyu.fi
- 139 Departamento de Sistemática e Ecologia, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, 58059-970 Paraíba, Brasil. daniellemachadovieira86@gmail.com
- 140 Departamento de Sistemática e Ecologia, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, 58059-970 Paraíba, Brasil. alinnegurjao@gmail.com
- 141 Department of Civil Engineering, University of A Coruña, 15192 A Coruña, Spain. jdelgado@udc.es
- 142 Department of Civil Engineering, University of A Coruña, 15192 A Coruña, Spain. david.morrondo@udc.es
- 143 Department of Civil Engineering, University of A Coruña, 15192 A Coruña, Spain. jose.cereijo@udc.es
- 144 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. jgoma@ub.edu
- 145 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. mctrapote84@gmail.com
- 146 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. tvegas@ub.edu
- 147 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. obrador@ub.edu
- 148 Department of Hydrobiology, University of Bialystok, 15245 Bialystok, Poland. magra@uwb.edu.pl
- 149 Department of Hydrobiology, University of Bialystok, 15245 Bialystok, Poland. m.karpowicz@uwb.edu.pl
- 150 Institute of Environmental Protection and Engineering, University of Bielsko-Biala, 43309 Bielsko-Biala, Poland. dachmura@gmail.com
- 151 Department of Biology, University of Cádiz, 11510 Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain. barbara.ubeda@uca.es
- 152 Department of Biology, University of Cádiz, 11510 Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain. joseangel.galvez@uca.es
- 153 Department of Forest Engineering, University of Cankiri Karatekin, 18200 Cankiri, Turkey. ardaozen@gmail.com
- 154 Freshwater Biological Laboratory, Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark. kchristoffersen@bio.ku.dk
- 155 Freshwater Biological Laboratory, Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark. twperlt@bio.ku.dk
- 156 Department of Marine Biotechnology, University of Gdansk, 81378 Gdynia, Poland. justyna.kobos@ug.edu.pl
- 157 Department of Marine Biotechnology, University of Gdansk, 81378 Gdynia, Poland. biohm@ug.edu.pl
- 158 Department of Ecology, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain. cperezm@ugr.es
- 159 Department of Ecology, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain. eloisa@ugr.es
- 160 Lammi Biological Station, University of Helsinki, 16900 Lammi, Finland. lauri.arvola@helsinki.fi
- 161 Department of Animal Biology, Plant Biology and Ecology, University of Jaen, 23701 Jaen, Spain. pabloalcarazparraga@gmail.com
- 162 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. magda.wis@interia.pl
- 163 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. barbara.pawlik@up.lublin.pl
- 164 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. michal.niedzwiecki@up.lublin.pl
- 165 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. wojciech.peczula@up.lublin.pl
- 166 Instituto Dom Luiz, University of Lisbon, 1749016 Lisbon, Portugal. mleira@fc.ul.pt
- 167 Institute of Earth Sciences Jaume Almera, ICTJA, CSIC, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. ahernandez@ictja.csic.es
- 168 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. quique@uma.es
- 169 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. jmblanco@uma.es
- 170 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. valeriano@uma.es
- 171 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. montesperezjj@gmail.com
- 172 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. rlpalomino@uma.es
- 173 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. stelax_rp@hotmail.com
- 174 Centro de Investigacións Cientificas Avanzadas (CICA), Facultade de Ciencias, Universidade da Coruña, 15071 A Coruña, Spain. r.carballeira@udc.es
- 175 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. antonio.camacho@uv.es
- 176 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. antonio.picazo-mozo@uv.es
- 177 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. carlos.rochera@uv.es
- 178 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. anna.santamans@gmail.com
- 179 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. carmen.ferriol@uv.es
- 180 Department of Microbiology and Ecology, University of Valencia, 46100 Burjassot, Spain. susana.romo@uv.es
- 181 Department of Microbiology and Ecology, University of Valencia, 46100 Burjassot, Spain. juan.soria@uv.es (J.M.S.)
- 182 Department ofWater Protection Engineering, University ofWarmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. julitad@uwm.edu.pl
- 183 Department ofWater Protection Engineering, University ofWarmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. justyna.sienska@uwm.edu.pl
- 184 Department ofWater Protection Engineering, University ofWarmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. daniel.szymanski@uwm.edu.pl
- 185 Department of Tourism, Recreation and Ecology, University of Warmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. mkruk@uwm.edu.pl
- 186 Faculty of Biology, University ofWarsaw, 02-096Warsaw, Poland. iwona.ks@biol.uw.edu.pl
- 187 Department of Plant Ecology and Environmental Conservation, Faculty of Biology, University ofWarsaw, 02-089 Warsaw, Poland. jasser.iwona@biol.uw.edu.pl
- 188 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia. petar.zutinic@biol.pmf.hr
- 189 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia. marija.gligora.udovic@biol.pmf.hr
- 190 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia. andjelka.plenkovic-moraj@biol.pmf.hr
- 191 Department of Environmental Improvement, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, 02-787Warsaw, Poland. magdalena_frak@sggw.pl
- 192 Department of Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, 02-787Warsaw, Poland. agnieszka_bankowska@sggw.pl
- 193 Department of Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, 02-787Warsaw, Poland. michal_wasilewicz@sggw.pl
- 194 Institute of Marine Sciences, Marine Biology and Fisheries, Middle East Technical University, 06800 Ankara, Turkey. okorhan@metu.edu.tr
- 195 Society for the Protection of Prespa, 53077 Agios Germanos, Greece. valentini.maliaka@gmail.com
- 196 Institute for Water and Wetland Research, Department of Aquatic Ecology and Environmental Biology, Radboud University Nijmegen, 6525 AJ Nijmegen, The Netherlands. valentini.maliaka@gmail.com
- 197 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. valentini.maliaka@gmail.com
- 198 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. kiti@ut.ee
- 199 Tartu Observatory, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Tartu, 61602 Tartu, Estonia. kiti@ut.ee
- 200 Department of Experimental Limnology, Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries, 16775 Stechlin, Germany. hgrossart@igb-berlin.de
- 201 Institute of Biochemistry and Biology, Potsdam University, 14469 Potsdam, Germany. hgrossart@igb-berlin.de
- 202 Institute of Marine Sciences, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC 28557, USA. hpaerl@email.unc.edu
- 203 Department of Biological Sciences, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA. cayelan@vt.edu
- 204 Department F.-A. Forel for Environmental and Aquatic Sciences, University of Geneva, 1205 Geneva, Switzerland. Bastiaan.Ibelings@unige.ch
- PMID: 29652856
- PMCID: PMC5923322
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10040156
Temperature Effects Explain Continental Scale Distribution of Cyanobacterial Toxins
Authors
Affiliations
- 1 Department F.-A. Forel for Environmental and Aquatic Sciences, University of Geneva, 1205 Geneva, Switzerland. Evanthia.Mantzouki@unige.ch.
- 2 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. miquel.lurling@wur.nl.
- 3 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. miquel.lurling@wur.nl.
- 4 German Environment Agency, Unit Drinking Water Resources and Water Treatment, Corrensplatz 1, 14195 Berlin, Germany. jutta.fastner@uba.de.
- 5 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.desenerpontdomis@nioo.knaw.nl.
- 6 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.desenerpontdomis@nioo.knaw.nl.
- 7 Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-120 Krakow, Poland. wilk@iop.krakow.pl.
- 8 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. judita.koreiviene@gmail.com
- 9 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.seelen@nioo.knaw.nl
- 10 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. l.seelen@nioo.knaw.nl
- 11 Department of Aquatic Ecology, Netherlands Institute of Ecology (NIOO-KNAW), 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. s.teurlincx@nioo.knaw.nl
- 12 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. yvonverstijnen@hotmail.com
- 13 Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-120 Krakow, Poland. krzton@iop.krakow.pl
- 14 Institute of Nature Conservation, Polish Academy of Sciences, 31-120 Krakow, Poland. walusiak@iop.krakow.pl
- 15 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. jurate.karosiene@botanika.lt
- 16 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. jurate.kasperoviciene@botanika.lt
- 17 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. ksenija.savadova@gamtostyrimai.lt
- 18 Institute of Botany, Nature Research Centre, Vilnius 08412, Lithuania. irma.vitonyte@gmail.com
- 19 R&D Department Environmental Engineering, 3edata, 27004 Lugo, Spain. carmen.cillero@3edata.es
- 20 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. ag.budzynska@gmail.com
- 21 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. rgold@amu.edu.pl
- 22 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. akozak@amu.edu.pl
- 23 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. rosinska.asia@gmail.com
- 24 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. eszelag@amu.edu.pl
- 25 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. domekp@amu.edu.pl
- 26 Department ofWater Protection, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. jakubowskan@gmail.com
- 27 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. kingakwasizur@wp.pl
- 28 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. messyasz@amu.edu.pl
- 29 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. ola.p@amu.edu.pl
- 30 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. marpel@amu.edu.pl
- 31 Department of Hydrobiology, Adam Mickiewicz University, 61614 Poznan, Poland. kok@amu.edu.pl
- 32 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. ana.garcia@aecom.com
- 33 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. montserrat.real@aecom.com
- 34 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. elvira.romans@aecom.com
- 35 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. jordi.noguero@aecom.com
- 36 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. parra1404@hotmail.com
- 37 Department of Limnology and Water Quality, AECOM U.R.S, 08036 Barcelona, Spain. elifdzmo@gmail.com
- 38 Department of Environmental Engineering, Abant Izzet Baysal University, 14280 Bolu, Turkey. karakaya_n@ibu.edu.tr
- 39 Department of Science and Engineering, Åbo Akademi University, 20520 Åbo, Finland. kerstin.haggqvist@gmail.com
- 40 Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture, Ankara University, 6100 Ankara, Turkey. nilsundemir2@gmail.com
- 41 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. meryem@metu.edu.tr
- 42 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. nrflzster@gmail.com
- 43 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. eti@thelevis.com
- 44 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. iskin.ugur@gmail.com
- 45 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. gizbezirci@gmail.com
- 46 Department of biology, Middle East Technical University, 6800 Ankara, Turkey. unyazgan@gmail.com
- 47 Institute of Marine Sciences, Department of Oceanography, Middle East Technical University, 06800 Ankara, Turkey. koray@ims.metu.edu.tr
- 48 Department of Botany, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece. sgkelis@bio.auth.gr
- 49 Department of Botany, Aristotle University of Thessaloniki, 54124 Thessaloniki, Greece. mattpano@bio.auth.gr
- 50 Department of Basic Science, Ataturk University, 25240 Erzurum, Turkey. ozden.fakioglu@atauni.edu.tr
- 51 Water Quality Department, Athens Water Supply and Sewerage Company, 11146 Athens, Greece. c.avagianos@icloud.com
- 52 Water Quality Department, Athens Water Supply and Sewerage Company, 11146 Athens, Greece. t_kaloudis@ath.forthnet.gr
- 53 Department of Biology, Balikesir University, 10145 Balikesir, Turkey. kcelik@balikesir.edu.tr
- 54 Department of Bioengineering, Bursa Technical University, 16310 Bursa, Turkey. mete.yilmaz@btu.edu.tr
- 55 Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA), 17003 Girona, Spain. rmarce@icra.cat
- 56 Catalan Institute for Water Research (ICRA), 17003 Girona, Spain. ncatalangarcia@gmail.com
- 57 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. ncatalangarcia@gmail.com
- 58 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. jandriugarcia@gmail.com
- 59 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. moritz.buck@ebc.uu.se
- 60 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. william.colom@ebc.uu.se
- 61 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. kristiina.mustonen@ebc.uu.se
- 62 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. don.pierson@ebc.uu.se
- 63 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Erken Laboratory, Uppsala University, 76173 Norrtalje, Sweden. yang.yang@hotmail.se
- 64 Research Center in Biodiversity and Genetic Resources (CIBIO-Azores), InBIO Associated Laboratory, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of the Azores, 9501-801 Ponta Delgada, Portugal. pedro.mv.raposeiro@uac.pt
- 65 Research Center in Biodiversity and Genetic Resources (CIBIO-Azores), InBIO Associated Laboratory, Faculty of Sciences and Technology, University of the Azores, 9501-801 Ponta Delgada, Portugal. vitor.mc.goncalves@uac.pt
- 66 Department of Environmental Science and Technology, Cyprus University of Technology, 3036 Lemesos, Cyprus. maria.antoniou@cut.ac.cy
- 67 Department of Environmental Science and Technology, Cyprus University of Technology, 3036 Lemesos, Cyprus. tsiarta.nikoletta@gmail.com
- 68 Centre for Freshwater and Environmental Studies, Dundalk Institute of Technology, A91 K584 Dundalk, Ireland. valerie.mccarthy@dkit.ie
- 69 Centre for Freshwater and Environmental Studies, Dundalk Institute of Technology, A91 K584 Dundalk, Ireland. victorc.perello@dkit.ie
- 70 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. tonu.feldmann@emu.ee
- 71 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. alo.laas@emu.ee
- 72 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. kristel.panksep@emu.ee
- 73 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. lea.tuvikene@emu.ee
- 74 European Regional Centre for Ecohydrology of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 90364 Lodz, Poland. ilonagagala@erce.unesco.lodz.pl
- 75 European Regional Centre for Ecohydrology of the Polish Academy of Sciences, 90364 Lodz, Poland. j.mankiewicz@erce.unesco.lodz.pl
- 76 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. meralyagci@gmail.com
- 77 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. sakircinar@gmail.com
- 78 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. kadircapkin32@hotmail.com
- 79 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. a.k.yagci58@gmail.com
- 80 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. mehmetcesur3232@gmail.com
- 81 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. fuatbilgin@gmail.com
- 82 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. caferbulut@gmail.com
- 83 Republic of Turkey Ministry of Food Agriculture, Fisheries Research Institute, 32500 Eğirdir, Isparta, Turkey. uysalrahmi@hotmail.com
- 84 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. ulrike.obertegger@fmach.it
- 85 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. adriano.boscaini@fmach.it
- 86 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. giovanna.flaim@fmach.it
- 87 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. nico.salmaso@fmach.it
- 88 Department of Sustainable Ecosystems and Bioresources, Fondazione Edmund Mach, 38010 San Michele all’Adige, Italy. leonardo.cerasino@fmach.it
- 89 Department of Biological and Environmental Sciences, University of Stirling, Stirling FK9 4LA, UK. jerich15@ceh.ac.uk
- 90 Department of Freshwater and Marine Ecology, University of Amsterdam, 1090 GE Amsterdam, The Netherlands. p.m.visser@uva.nl
- 91 Department of Freshwater and Marine Ecology, University of Amsterdam, 1090 GE Amsterdam, The Netherlands. j.m.h.verspagen@uva.nl
- 92 Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Gaziosmanpasa University, 60250 Merkez, Turkey. biyo_tunay@hotmail.com
- 93 Department of Biology, Giresun University, 28100 Giresun, Turkey. elif.neyran.soylu@giresun.edu.tr
- 94 Department of Biology, Hitit University, 19040 Corum, Turkey. farukmaraslioglu@hitit.edu.tr
- 95 Department of Icthyology, Hydrobiology and Aquatic Ecology, Inland Fisheries Institute, 10719 Olsztyn, Poland. a.napiorkowska-krzebietke@infish.com.pl
- 96 Department of Freshwater Protection, Institute of Environmental Protection- National Research Institute, 01-692 Warsaw, Poland. a.ochocka@ios.edu.pl
- 97 Department of Freshwater Protection, Institute of Environmental Protection- National Research Institute, 01-692 Warsaw, Poland. paszta@ios.edu.pl
- 98 Centro de Investigação da Montanha, Instituto Politécnico de Bragança, Campus de Santa Apolónia, 5300-253 Bragança, Portugal; geraldes@ipb.pt
- 99 Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR) and University of Porto, 4450-208 Matosinhos, Portugal. vmvascon@fc.up.pt
- 100 Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR) and University of Porto, 4450-208 Matosinhos, Portugal. joaopmorais@gmail.com
- 101 Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR) and University of Porto, 4450-208 Matosinhos, Portugal. mica.ciimar@gmail.com
- 102 Department of Freshwater Resource and Management, Faculty of Aquatic Sciences, Istanbul University, 34134 Istanbul, Turkey. latifekoker@gmail.com
- 103 Department of Freshwater Resource and Management, Faculty of Aquatic Sciences, Istanbul University, 34134 Istanbul, Turkey. rakcaalan@gmail.com
- 104 Department of Freshwater Resource and Management, Faculty of Aquatic Sciences, Istanbul University, 34134 Istanbul, Turkey. albay.hermano@gmail.com
- 105 Department of Biology, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, 31000 Osijek, Croatia. dspoljaric@biologija.unios.hr
- 106 Department of Biology, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, 31000 Osijek, Croatia. fstevic@biologija.unios.hr
- 107 Department of Biology, Josip Juraj Strossmayer University of Osijek, 31000 Osijek, Croatia. tzuna@biologija.unios.hr
- 108 Department of Experimental Limnology, Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries, 16775 Stechlin, Germany. fonvielle@igb-berlin.de
- 109 Department of Biology, Limnological Institute, University of Konstanz, 78464 Konstanz, Germany. dietmar.straile@uni-konstanz.de
- 110 Department of Biology, Limnological Institute, University of Konstanz, 78464 Konstanz, Germany. karl.rothhaupt@uni-konstanz.de
- 111 Department of Biology, Lund University, 22362 Lund, Sweden. lars-anders.hansson@biol.lu.se
- 112 Department of Ecology and Genetics, Limnology, Uppsala University, 75236 Uppsala, Sweden. pablo.urrutia_cordero@biol.lu.se
- 113 Department of Biology, Lund University, 22362 Lund, Sweden. pablo.urrutia_cordero@biol.lu.se
- 114 RECETOX, Faculty of Science, Masaryk University, 62500 Brno, Czech Republic. blaha@recetox.muni.cz
- 115 Department of Hydrobiology, Morava Board Authority, 60200 Brno, Czech Republic. geris@pmo.cz
- 116 Laboratory of Paleoecology, Institute of Botany, The Czech Academy of Sciences, 60200 Brno, Czech Republic. marketka.kozakova@seznam.cz
- 117 Department of Environment and Resource Management, Mediterranean Fisheries Research Production and Training Institute, 7090 Antalya, Turkey. matkocer@hotmail.com
- 118 Faculty of Aquaculture, Mersin University, 33160 Mersin, Turkey. talp@mersin.edu.tr
- 119 Department ofWater Quality, Slovenian Environmental Agency, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia. spela.remec-rekar@gov.si
- 120 Department of Genetic Toxicology and Cancer Biology, National Institute of Biology, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia. tina.elersek@nib.si
- 121 Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, National Center for Scientific Research «DEMOKRITOS», 15341 Attiki, Greece. t.triantis@inn.demokritos.gr
- 122 Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, National Center for Scientific Research «DEMOKRITOS», 15341 Attiki, Greece. s.zervou@inn.demokritos.gr
- 123 Institute of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology, National Center for Scientific Research «DEMOKRITOS», 15341 Attiki, Greece. a.hiskia@inn.demokritos.gr
- 124 Department of Freshwater Ecology, Norwegian Institute for Water Research, 0349 Oslo, Norway. sigrid.haande@niva.no
- 125 Department of Freshwater Ecology, Norwegian Institute for Water Research, 0349 Oslo, Norway. birger.skjelbred@niva.no
- 126 Institute of Environmental Engineering, Poznan University of Technology, 60965 Poznan, Poland. beata.madrecka@put.poznan.pl
- 127 National Reference Center for Hydrobiology, Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic, 82645 Bratislava, Slovakia. hana.nemova@uvzsr.sk
- 128 National Reference Center for Hydrobiology, Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic, 82645 Bratislava, Slovakia. iveta.drastichova@uvzsr.sk
- 129 National Reference Center for Hydrobiology, Public Health Authority of the Slovak Republic, 82645 Bratislava, Slovakia. lucia.chomova@uvzsr.sk
- 130 School of Pharmacy and Life Sciences, Robert Gordon University, Aberdeen AB10 7GJ, UK. c.edwards@rgu.ac.uk
- 131 Department of Biology, Sakarya University, 54187 Sakarya, Turkey. tsevindik@sakarya.edu.tr
- 132 Department of Biology, Sakarya University, 54187 Sakarya, Turkey. htunca@sakarya.edu.tr
- 133 Department of Biology, Sakarya University, 54187 Sakarya, Turkey. burcin.onem1@ogr.sakarya.edu.tr
- 134 Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, SS Cyril and Methodius University, 1000 Skopje, Macedonia. borisaleksovski@pmf.ukim.mk
- 135 Faculty of Natural Sciences and Mathematics, SS Cyril and Methodius University, 1000 Skopje, Macedonia. skrstic@pmf.ukim.mk
- 136 Department for Ecotoxicology, Teaching Institute of Public Health of Primorje-Gorski Kotar County, 51000 Rijeka, Croatia. itana.bokan@zzjzpgz.hr
- 137 Institute of Technology, The State University of Applied Sciences, 82300 Elblag, Poland. nawrocka.lidia@op.pl
- 138 Department of Biological and Environmental Science, University of Jyväskylä, 40014 Jyväskylä, Finland. pauliina.u.m.salmi@jyu.fi
- 139 Departamento de Sistemática e Ecologia, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, 58059-970 Paraíba, Brasil. daniellemachadovieira86@gmail.com
- 140 Departamento de Sistemática e Ecologia, Universidade Federal da Paraíba, 58059-970 Paraíba, Brasil. alinnegurjao@gmail.com
- 141 Department of Civil Engineering, University of A Coruña, 15192 A Coruña, Spain. jdelgado@udc.es
- 142 Department of Civil Engineering, University of A Coruña, 15192 A Coruña, Spain. david.morrondo@udc.es
- 143 Department of Civil Engineering, University of A Coruña, 15192 A Coruña, Spain. jose.cereijo@udc.es
- 144 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. jgoma@ub.edu
- 145 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. mctrapote84@gmail.com
- 146 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. tvegas@ub.edu
- 147 Department of Evolutionary Biology, Ecology, and Environmental Sciences, University of Barcelona, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. obrador@ub.edu
- 148 Department of Hydrobiology, University of Bialystok, 15245 Bialystok, Poland. magra@uwb.edu.pl
- 149 Department of Hydrobiology, University of Bialystok, 15245 Bialystok, Poland. m.karpowicz@uwb.edu.pl
- 150 Institute of Environmental Protection and Engineering, University of Bielsko-Biala, 43309 Bielsko-Biala, Poland. dachmura@gmail.com
- 151 Department of Biology, University of Cádiz, 11510 Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain. barbara.ubeda@uca.es
- 152 Department of Biology, University of Cádiz, 11510 Puerto Real, Cádiz, Spain. joseangel.galvez@uca.es
- 153 Department of Forest Engineering, University of Cankiri Karatekin, 18200 Cankiri, Turkey. ardaozen@gmail.com
- 154 Freshwater Biological Laboratory, Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark. kchristoffersen@bio.ku.dk
- 155 Freshwater Biological Laboratory, Department of Biology, University of Copenhagen, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark. twperlt@bio.ku.dk
- 156 Department of Marine Biotechnology, University of Gdansk, 81378 Gdynia, Poland. justyna.kobos@ug.edu.pl
- 157 Department of Marine Biotechnology, University of Gdansk, 81378 Gdynia, Poland. biohm@ug.edu.pl
- 158 Department of Ecology, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain. cperezm@ugr.es
- 159 Department of Ecology, University of Granada, 18071 Granada, Spain. eloisa@ugr.es
- 160 Lammi Biological Station, University of Helsinki, 16900 Lammi, Finland. lauri.arvola@helsinki.fi
- 161 Department of Animal Biology, Plant Biology and Ecology, University of Jaen, 23701 Jaen, Spain. pabloalcarazparraga@gmail.com
- 162 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. magda.wis@interia.pl
- 163 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. barbara.pawlik@up.lublin.pl
- 164 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. michal.niedzwiecki@up.lublin.pl
- 165 Department of Hydrobiology and Protection of Ecosystems, University of Life Sciences in Lublin, 20262 Lublin, Poland. wojciech.peczula@up.lublin.pl
- 166 Instituto Dom Luiz, University of Lisbon, 1749016 Lisbon, Portugal. mleira@fc.ul.pt
- 167 Institute of Earth Sciences Jaume Almera, ICTJA, CSIC, 08028 Barcelona, Spain. ahernandez@ictja.csic.es
- 168 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. quique@uma.es
- 169 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. jmblanco@uma.es
- 170 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. valeriano@uma.es
- 171 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. montesperezjj@gmail.com
- 172 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. rlpalomino@uma.es
- 173 Department of Ecology, University of Malaga, 29071 Malaga, Spain. stelax_rp@hotmail.com
- 174 Centro de Investigacións Cientificas Avanzadas (CICA), Facultade de Ciencias, Universidade da Coruña, 15071 A Coruña, Spain. r.carballeira@udc.es
- 175 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. antonio.camacho@uv.es
- 176 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. antonio.picazo-mozo@uv.es
- 177 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. carlos.rochera@uv.es
- 178 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. anna.santamans@gmail.com
- 179 Cavanilles Institute of Biodiversity and Evolutionary Biology, University of Valencia, 46980 Paterna Valencia, Spain. carmen.ferriol@uv.es
- 180 Department of Microbiology and Ecology, University of Valencia, 46100 Burjassot, Spain. susana.romo@uv.es
- 181 Department of Microbiology and Ecology, University of Valencia, 46100 Burjassot, Spain. juan.soria@uv.es (J.M.S.)
- 182 Department ofWater Protection Engineering, University ofWarmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. julitad@uwm.edu.pl
- 183 Department ofWater Protection Engineering, University ofWarmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. justyna.sienska@uwm.edu.pl
- 184 Department ofWater Protection Engineering, University ofWarmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. daniel.szymanski@uwm.edu.pl
- 185 Department of Tourism, Recreation and Ecology, University of Warmia and Mazury, 10-720 Olsztyn, Poland. mkruk@uwm.edu.pl
- 186 Faculty of Biology, University ofWarsaw, 02-096Warsaw, Poland. iwona.ks@biol.uw.edu.pl
- 187 Department of Plant Ecology and Environmental Conservation, Faculty of Biology, University ofWarsaw, 02-089 Warsaw, Poland. jasser.iwona@biol.uw.edu.pl
- 188 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia. petar.zutinic@biol.pmf.hr
- 189 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia. marija.gligora.udovic@biol.pmf.hr
- 190 Department of Biology, Faculty of Science, University of Zagreb, 10000 Zagreb, Croatia. andjelka.plenkovic-moraj@biol.pmf.hr
- 191 Department of Environmental Improvement, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, 02-787Warsaw, Poland. magdalena_frak@sggw.pl
- 192 Department of Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, 02-787Warsaw, Poland. agnieszka_bankowska@sggw.pl
- 193 Department of Hydraulic Engineering, Faculty of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Warsaw University of Life Sciences—SGGW, 02-787Warsaw, Poland. michal_wasilewicz@sggw.pl
- 194 Institute of Marine Sciences, Marine Biology and Fisheries, Middle East Technical University, 06800 Ankara, Turkey. okorhan@metu.edu.tr
- 195 Society for the Protection of Prespa, 53077 Agios Germanos, Greece. valentini.maliaka@gmail.com
- 196 Institute for Water and Wetland Research, Department of Aquatic Ecology and Environmental Biology, Radboud University Nijmegen, 6525 AJ Nijmegen, The Netherlands. valentini.maliaka@gmail.com
- 197 Department of Environmental Sciences, Wageningen University & Research, 6700 Wageningen, The Netherlands. valentini.maliaka@gmail.com
- 198 Institute of Agricultural and Environmental Sciences, Estonian University of Life Sciences, 51014 Tartu, Estonia. kiti@ut.ee
- 199 Tartu Observatory, Faculty of Science and Technology, University of Tartu, 61602 Tartu, Estonia. kiti@ut.ee
- 200 Department of Experimental Limnology, Leibniz Institute of Freshwater Ecology and Inland Fisheries, 16775 Stechlin, Germany. hgrossart@igb-berlin.de
- 201 Institute of Biochemistry and Biology, Potsdam University, 14469 Potsdam, Germany. hgrossart@igb-berlin.de
- 202 Institute of Marine Sciences, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC 28557, USA. hpaerl@email.unc.edu
- 203 Department of Biological Sciences, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, VA 24061, USA. cayelan@vt.edu
- 204 Department F.-A. Forel for Environmental and Aquatic Sciences, University of Geneva, 1205 Geneva, Switzerland. Bastiaan.Ibelings@unige.ch
- PMID: 29652856
- PMCID: PMC5923322
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10040156
Abstract
Insight into how environmental change determines the production and distribution of cyanobacterial toxins is necessary for risk assessment. Management guidelines currently focus on hepatotoxins (microcystins). Increasing attention is given to other classes, such as neurotoxins (e.g., anatoxin-a) and cytotoxins (e.g., cylindrospermopsin) due to their potency. Most studies examine the relationship between individual toxin variants and environmental factors, such as nutrients, temperature and light. In summer 2015, we collected samples across Europe to investigate the effect of nutrient and temperature gradients on the variability of toxin production at a continental scale. Direct and indirect effects of temperature were the main drivers of the spatial distribution in the toxins produced by the cyanobacterial community, the toxin concentrations and toxin quota. Generalized linear models showed that a Toxin Diversity Index (TDI) increased with latitude, while it decreased with water stability. Increases in TDI were explained through a significant increase in toxin variants such as MC-YR, anatoxin and cylindrospermopsin, accompanied by a decreasing presence of MC-LR. While global warming continues, the direct and indirect effects of increased lake temperatures will drive changes in the distribution of cyanobacterial toxins in Europe, potentially promoting selection of a few highly toxic species or strains.
Keywords: European Multi Lake Survey; anatoxin; cylindrospermopsin; direct effects; indirect effects; microcystin; spatial distribution; temperature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
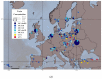
Figure 1
Percentages of ( a )…
Figure 1
Percentages of ( a ) toxin concentrations (μg/L) and ( b ) toxin…

Figure 1
Percentages of ( a )…
Figure 1
Percentages of ( a ) toxin concentrations (μg/L) and ( b ) toxin…
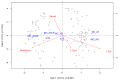
Figure 2
RDA biplot of the toxin…
Figure 2
RDA biplot of the toxin quota (toxin μg/chlorophyll-a μg; Hellinger transformed due to…
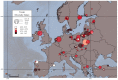
Figure 3
Map of the Toxin Diversity…
Figure 3
Map of the Toxin Diversity Index (TDI) of the 137 EMLS lakes, calculated…
References
-
- Codd G.A., Meriluoto J., Metcalf J.S. Handbook of Cyanobacterial Monitoring and Cyanotoxin Analysis. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2017. Introduction: Cyanobacteria, Cyanotoxins, Their Human Impact, and Risk Management.
-
- Huisman J.M., Matthijs H.C.P., Visser P.M. Harmful Cyanobacteria. Springer Aquatic Ecology Series 3. Springer; Dordrecht, The Netherlands: 2005. p. 243.
-
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) Loss and Damage: The role of Ecosystem Services. United Nations Environment Programme. UNEP; Nairobi, Kenya: 2016.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

