Virtual screening by a new Clustering-based Weighted Similarity Extreme Learning Machine approach
- PMID: 29652912
- PMCID: PMC5898726
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195478
Virtual screening by a new Clustering-based Weighted Similarity Extreme Learning Machine approach
Abstract
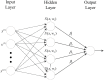
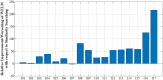
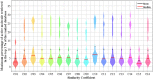
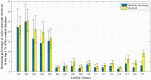
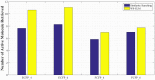
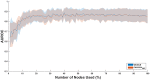
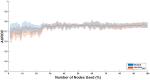
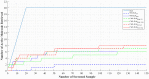
Machine learning techniques are becoming popular in virtual screening tasks. One of the powerful machine learning algorithms is Extreme Learning Machine (ELM) which has been applied to many applications and has recently been applied to virtual screening. We propose the Weighted Similarity ELM (WS-ELM) which is based on a single layer feed-forward neural network in a conjunction of 16 different similarity coefficients as activation function in the hidden layer. It is known that the performance of conventional ELM is not robust due to random weight selection in the hidden layer. Thus, we propose a Clustering-based WS-ELM (CWS-ELM) that deterministically assigns weights by utilising clustering algorithms i.e. k-means clustering and support vector clustering. The experiments were conducted on one of the most challenging datasets-Maximum Unbiased Validation Dataset-which contains 17 activity classes carefully selected from PubChem. The proposed algorithms were then compared with other machine learning techniques such as support vector machine, random forest, and similarity searching. The results show that CWS-ELM in conjunction with support vector clustering yields the best performance when utilised together with Sokal/Sneath(1) coefficient. Furthermore, ECFP_6 fingerprint presents the best results in our framework compared to the other types of fingerprints, namely ECFP_4, FCFP_4, and FCFP_6.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
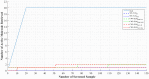
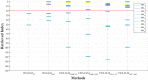
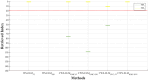
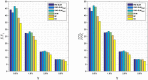
Similar articles
-
Spoken language identification based on the enhanced self-adjusting extreme learning machine approach.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 19;13(4):e0194770. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194770. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29672546 Free PMC article.
-
Brain tumor segmentation approach based on the extreme learning machine and significantly fast and robust fuzzy C-means clustering algorithms running on Raspberry Pi hardware.Med Hypotheses. 2020 Mar;136:109507. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2019.109507. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Med Hypotheses. 2020. PMID: 31812927
-
Extreme Learning Machine Framework for Risk Stratification of Fatty Liver Disease Using Ultrasound Tissue Characterization.J Med Syst. 2017 Aug 23;41(10):152. doi: 10.1007/s10916-017-0797-1. J Med Syst. 2017. PMID: 28836045
-
Performance of machine learning methods for ligand-based virtual screening.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009 May;12(4):358-68. doi: 10.2174/138620709788167962. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009. PMID: 19442065 Review.
-
Machine learning in virtual screening.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009 May;12(4):332-43. doi: 10.2174/138620709788167980. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2009. PMID: 19442063 Review.
Cited by
-
PubChem in 2021: new data content and improved web interfaces.Nucleic Acids Res. 2021 Jan 8;49(D1):D1388-D1395. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa971. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021. PMID: 33151290 Free PMC article.
-
SELM: Siamese extreme learning machine with application to face biometrics.Neural Comput Appl. 2022;34(14):12143-12157. doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07100-z. Epub 2022 Mar 15. Neural Comput Appl. 2022. PMID: 35310555 Free PMC article.
-
Based on Virtual Screening and Simulation Exploring the Mechanism of Plant-Derived Compounds with PINK1 to Postherpetic Neuralgia.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):9184-9203. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04098-4. Epub 2024 Apr 11. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38602654
-
Design and bioactivity evaluation of a novel autotaxin inhibitor with anti-hepatic fibrosis effects.Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 1;15(1):11092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-95464-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40169822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leach AR, Gillet VJ. An Introduction to Chemoinformatics. Springer; Netherlands; 2007.
-
- Wilton DJ, Harrison RF, Willett P, Delaney J, Lawson K, Mullier G. Virtual Screening Using Binary Kernel Discrimination: Analysis of Pesticide Data. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2006;46(2):471–477. doi: 10.1021/ci050397w - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pasupa K, Hussain Z, Shawe-Taylor J, Willett P. Drug Screening with Elastic-Net Multiple Kernel Learning. In: Proceeding of the 13th IEEE International Conference on BioInformatics and BioEngineering (BIBE 2013), 10–13 November 2013, Chania, Greece; 2013. p. 1–5.
-
- Kurczab R, Bojarski AJ. The influence of the negative-positive ratio and screening database size on the performance of machine learning-based virtual screening. PloS One. 2017;12(4):e0175410 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0175410 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen B, Harrison RF, Pasupa K, Willett P, Wilton DJ, Wood DJ, et al. Virtual Screening Using Binary Kernel Discrimination: Effect of Noisy Training Data and the Optimization of Performance. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 2006;46(2):478–486. doi: 10.1021/ci0505426 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

