Kinetics of IgM and IgG antibodies after scrub typhus infection and the clinical implications
- PMID: 29653201
- PMCID: PMC5985369
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.03.018
Kinetics of IgM and IgG antibodies after scrub typhus infection and the clinical implications
Abstract
Objectives: The serological detection of IgM antibodies is the most widely used test to diagnose scrub typhus infection. However, the kinetics of IgM and IgG antibodies post-infection remain elusive, which could contribute to false positivity. The objective of this study was to document the nature of the evolution of these antibody titres after infection.
Methods: Adult patients previously confirmed to have scrub typhus by IgM ELISA, positive PCR, or both, were included in this cross-sectional study. The levels of IgM and IgG antibodies in serum samples were tested using an ELISA and the distribution curve was plotted.
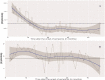
Results: Two hundred and three patients were included in this study. Post-infection serum sampling was done between 1 month and 46 months after documented infection. IgM levels declined gradually but remained elevated above the diagnostic cut-off for up to 12 months post-infection. However, IgG levels continued to rise reaching a peak at 10 months, followed by a gradual decline over several months. In the majority of cases, the IgG levels remained above the cut-off threshold for more than 36 months.
Conclusions: Clinicians need to be cautious in using a single serum sample for the detection of IgM to diagnose scrub typhus, as it remains elevated for up to 12 months after the infection, whereas the serum IgG level could be used as an indicator of past infection.
Keywords: IgG; IgM; Kinetics; Orientia tsutsugamushi; Rickettsia; Scrub typhus.
Copyright © 2018 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Blacksell Stuart D., Bryant Naomi J., Paris Daniel H., Doust Jenny A., Sakoda Yoshihiro, Day Nicholas P.J. Scrub typhus serologic testing with the indirect immunofluorescence method as a diagnostic gold standard: a lack of consensus leads to a lot of confusion. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(3):391–401. - PubMed
-
- Blacksell Stuart D., Tanganuchitcharnchai Ampai, Nawtaisong Pruksa, Kantipong Pacharee, Laongnualpanich Achara, Day Nicholas P.J. Diagnostic accuracy of the InBios scrub typhus detect enzyme-linked immunoassay for the detection of IgM antibodies in Northern Thailand. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2015;23(2):148–154. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen Hua-Wei, Zhang Zhiwen, Huber Erin, Mutumanje Elissa, Chao Chien-Chung, Ching Wei-Mei. Kinetics and magnitude of antibody responses against the conserved 47-kilodalton antigen and the variable 56-kilodalton antigen in scrub typhus patients. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2011;18(6):1021–1027. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Janardhanan Jeshina, Trowbridge Paul, Varghese George M. Diagnosis of scrub typhus. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2014;12(12):1533–1540. - PubMed
-
- Kim D.M., Lee Y.M., Back J.H., Yang T.Y., Lee J.H., Song H.J. A serosurvey of Orientia tsutsugamushi from patients with scrub typhus. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2010;16(5):447–451. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous