Role of PD-1 during effector CD8 T cell differentiation
- PMID: 29654146
- PMCID: PMC5939075
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1718217115
Role of PD-1 during effector CD8 T cell differentiation
Abstract
PD-1 (programmed cell death-1) is the central inhibitory receptor regulating CD8 T cell exhaustion during chronic viral infection and cancer. Interestingly, PD-1 is also expressed transiently by activated CD8 T cells during acute viral infection, but the role of PD-1 in modulating T cell effector differentiation and function is not well defined. To address this question, we examined the expression kinetics and role of PD-1 during acute lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection of mice. PD-1 was rapidly up-regulated in vivo upon activation of naive virus-specific CD8 T cells within 24 h after LCMV infection and in less than 4 h after peptide injection, well before any cell division had occurred. This rapid PD-1 expression by CD8 T cells was driven predominantly by antigen receptor signaling since infection with a LCMV strain with a mutation in the CD8 T cell epitope did not result in the increase of PD-1 on antigen-specific CD8 T cells. Blockade of the PD-1 pathway using anti-PD-L1 or anti-PD-1 antibodies during the early phase of acute LCMV infection increased mTOR signaling and granzyme B expression in virus-specific CD8 T cells and resulted in faster clearance of the infection. These results show that PD-1 plays an inhibitory role during the naive-to-effector CD8 T cell transition and that the PD-1 pathway can also be modulated at this stage of T cell differentiation. These findings have implications for developing therapeutic vaccination strategies in combination with PD-1 blockade.
Keywords: CD8 T cells; PD-1; effector differentiation; memory cells; viral infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: R.A. has patents on the PD-1 pathway and has served on the advisory board for Genentech/Roche and received research funding from Genentech and Merck. G.J.F. and A.H.S. have patents/pending royalties on the PD-1 pathway from Roche, Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, EMD Serono, Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, Dako, and Novartis. G.J.F. has served on advisory boards for Roche, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Xios, and Quiet. A.H.S. has served on advisory boards for Novartis, Surface Oncology, and Elstar. A.H.S. has received research funding from Novartis, Roche, UCB, Ipsen, and Quark. B.I.A. is an employee of Five Prime Therapeutics.
Figures
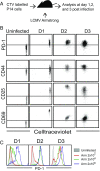


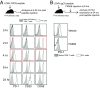
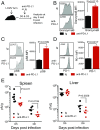

References
-
- Ahmed R, Gray D. Immunological memory and protective immunity: Understanding their relation. Science. 1996;272:54–60. - PubMed
-
- Kaech SM, et al. Selective expression of the interleukin 7 receptor identifies effector CD8 T cells that give rise to long-lived memory cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:1191–1198. - PubMed
-
- Kaech SM, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R. Effector and memory T-cell differentiation: Implications for vaccine development. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2:251–262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

