Predictors of Mortality and Symptomatic Outcome of Patients With Low-Flow Severe Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
- PMID: 29654191
- PMCID: PMC6015421
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.007977
Predictors of Mortality and Symptomatic Outcome of Patients With Low-Flow Severe Aortic Stenosis Undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement
Abstract
Background: Impaired left ventricular (LV) ejection fraction is a common finding in patients with aortic stenosis and serves as a predictor of morbidity and mortality after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. However, conflicting data on the most accurate measure for LV function exist. We wanted to examine the impact of LV ejection fraction, mean pressure gradient, and stroke volume index on the outcome of patients treated by transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
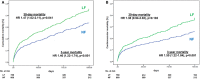
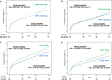
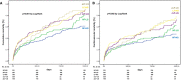
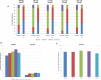
Methods and results: Patients treated by transcatheter aortic valve replacement were primarily separated into normal flow (NF; stroke volume index >35 mL/m2) and low flow (LF; stroke volume index ≤35 mL/m2). Afterwards, patients were divided into 5 groups: "NF-high gradient," "NF-low gradient" (NF-LG), "LF-high gradient," "paradoxical LF-LG," and "classic LF-LG." The 3-year mortality was the primary end point. Of 1600 patients, 789 (49.3%) were diagnosed as having LF, which was characterized by a higher 30-day (P=0.041) and 3-year (P<0.001) mortality. LF was an independent predictor of all-cause (hazard ratio, 1.29; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.62; P=0.03) and cardiovascular (hazard ratio, 1.37; 95% confidence interval, 1.06-1.77; P=0.016) mortality. Neither mean pressure gradient nor LV ejection fraction was an independent predictor of mortality. Patients with paradoxical LF-LG (35.0%), classic LF-LG (35.1%) and LF-high gradient (38.1%) had higher all-cause mortality at 3 years compared with NF-high gradient (24.8%) and NF-LG (27.9%) (P=0.001). However, surviving patients showed a similar improvement in symptoms regardless of aortic stenosis entity.
Conclusions: LF is a common finding within the aortic stenosis population and, in contrast to LV ejection fraction or mean pressure gradient, an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Despite increased long-term mortality, high procedural success and excellent functional improvement support transcatheter aortic valve replacement in patients with LF severe aortic stenosis.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; low flow; outcome; transcatheter aortic valve implantation; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
© 2018 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley.
Figures
Comment in
-
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement in Low-Flow Aortic Stenosis: Treat the Flow or Treat the Patient?J Am Heart Assoc. 2018 Apr 13;7(8):e008932. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.118.008932. J Am Heart Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29654200 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Herrmann HC, Pibarot P, Hueter I, Gertz ZM, Stewart WJ, Kapadia S, Tuzcu EM, Babaliaros V, Thourani V, Szeto WY, Bavaria JE, Kodali S, Hahn RT, Williams M, Miller DC, Douglas PS, Leon MB. Predictors of mortality and outcomes of therapy in low‐flow severe aortic stenosis: a Placement of Aortic Transcatheter Valves (PARTNER) trial analysis. Circulation. 2013;127:2316–2326. - PubMed
-
- Ding WH, Lam YY, Duncan A, Li W, Lim E, Kaya MG, Chung R, Pepper JR, Henein MY. Predictors of survival after aortic valve replacement in patients with low‐flow and high‐gradient aortic stenosis. Eur J Heart Fail. 2009;11:897–902. - PubMed
-
- Halkos ME, Chen EP, Sarin EL, Kilgo P, Thourani VH, Lattouf OM, Vega JD, Morris CD, Vassiliades T, Cooper WA, Guyton RA, Puskas JD. Aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis in patients with left ventricular dysfunction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:746–751. - PubMed
-
- Kuwaki K, Amano A, Inaba H, Yamamoto T, Matsumura T, Dohi S, Matsushita S. Predictors of early and mid‐term results in contemporary aortic valve replacement for aortic stenosis. J Card Surg. 2012;27:139–145. - PubMed
-
- Wendt D, Osswald BR, Kayser K, Thielmann M, Tossios P, Massoudy P, Kamler M, Jakob H. Society of Thoracic Surgeons score is superior to the EuroSCORE determining mortality in high risk patients undergoing isolated aortic valve replacement. Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88:468–474. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

