Antihypertensive effect of etamicastat in dopamine D2 receptor-deficient mice
- PMID: 29654295
- PMCID: PMC6503839
- DOI: 10.1038/s41440-018-0041-5
Antihypertensive effect of etamicastat in dopamine D2 receptor-deficient mice
Abstract
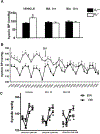
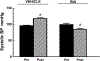
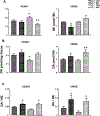
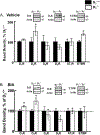
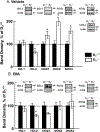
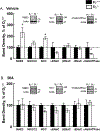
Abnormalities of the D2R gene (DRD2) play a role in the pathogenesis of human essential hypertension; variants of the DRD2 have been reported to be associated with hypertension. Disruption of Drd2 (D2-/-) in mice increases blood pressure. The hypertension of D2-/- mice has been related, in part, to increased sympathetic activity, renal oxidative stress, and renal endothelin B receptor (ETBR) expression. We tested in D2-/- mice the effect of etamicastat, a reversible peripheral inhibitor of dopamine-β-hydroxylase that reduces the biosynthesis of norepinephrine from dopamine and decreases sympathetic nerve activity. Blood pressure was measured in anesthetized D2-/- mice treated with etamicastat by gavage, (10 mg/kg), conscious D2-/- mice, and D2+/+ littermates, and mice with the D2R selectively silenced in the kidney, treated with etamicastat in the drinking water (10 mg/kg per day). Tissue and urinary catecholamines and renal expression of selected G protein-coupled receptors, enzymes related to the production of reactive oxygen species, and sodium transporters were also measured. Etamicastat decreased blood pressure both in anesthetized and conscious D2-/- mice and mice with renal-selective silencing of D2R to levels similar or close to those measured in D2+/+ littermates. Etamicastat decreased cardiac and renal norepinephrine and increased cardiac and urinary dopamine levels in D2-/- mice. It also normalized the increased renal protein expressions of ETBR, NADPH oxidase isoenzymes, and urinary 8-isoprostane, as well as renal NHE3 and NCC, and increased the renal expression of D1R but not D5R in D2-/- mice. In conclusion, etamicastat is effective in normalizing the increased blood pressure and some of the abnormal renal biochemical alterations of D2-/- mice.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
Figures
References
-
- Beliaev A, Learmonth DA, Soares-da-Silva P. Synthesis and biological evaluation of novel, peripherally selective chromanyl imidazolethione-based inhibitors of dopamine beta hydroxylase. JMed Chem. 2006: 49:1191–1197 - PubMed
-
- James PA, Oparil S, Carter BL, Cushman WC, Dennison-Himmelfarb C, Handler J, Lackland DT, LeFevre ML, MacKenzie TD, Ogedegbe O, Smith SC Jr, Svetkey LP, Taler SJ, Townsend RR, Wright JT Jr, Narva AS, Ortiz E. 2014. evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8). JAMA 2014: 311:507–520. - PubMed
-
- Igreja B, Pires NM, Bonifacio MJ, Loureiro AI, Fernandes-Lopes C, Wright LC, Soares-da-Silva P. Blood pressure-decreasing effect of etamicastat alone and in combination with antihypertensive drugs in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Hypertens Res 2015;38:30–38. - PubMed
-
- Igreja B, Wright L, Soares-da-Silva P. Sustained high blood pressure reduction with etamicastat, a selective peripheral dopamine-β-hydroxylase inhibitor. J Am Soc Hypertens 2016;10:207–216.. - PubMed
-
- Almeida L, Nunes T, Costa R, Rocha JF, Vaz-da-Silva M, Soares-da-Silva P. Etamicastat, a novel dopamine ß-hydroxylase inhibitor: tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics in patients with hypertension. Clin Ther. 2013:35:1983–1996. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

