Autistic Traits in Treatment-Seeking Transgender Adults
- PMID: 29654452
- PMCID: PMC6223809
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-018-3557-2
Autistic Traits in Treatment-Seeking Transgender Adults
Abstract
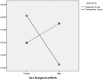
The present study aimed to compare prevalence of autistic traits measured by the self-reported autism spectrum quotient-short (AQ-short) in a transgender clinical population (n = 656) matched by age and sex assigned at birth to a cisgender community sample. Results showed that transgender and cisgender people reported similar levels of possible autistic caseness. Transgender people assigned female were more likely to have clinically significant autistic traits compared to any other group. No difference was found between those assigned male. High AQ scores may not be indicative of the presence of an autism spectrum condition as the difference between groups mainly related to social behaviours; such scores may be a reflection of transgender people's high social anxiety levels due to negative past experiences.
Keywords: Autism spectrum conditions; Autism spectrum quotient (AQ); Autistic traits; Social anxiety; Social issues; Transgender.
Figures
References
-
- Allison C, Auyeung B, Baron-Cohen S. Toward brief “red flags” for autism screening: The short autism spectrum quotient and the short quantitative checklist for autism in toddlers in 1,000 cases and 3,000 controls. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 2012;51:202–212. doi: 10.1016/j.jaac.2011.11.003. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association (APA) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
-
- Baron-Cohen S. Precursors to a theory of mind: Understanding attention in others. In: Whiten A, editor. Natural theories of mind: Evolution, development and simulation of everyday mindreading. Oxford: Basil Blackwell; 1991. pp. 233–251.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous