Outcomes of Early Liver Transplantation for Patients With Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis
- PMID: 29655837
- PMCID: PMC6460480
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.04.009
Outcomes of Early Liver Transplantation for Patients With Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis
Abstract
Background & aims: The American Consortium of Early Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Hepatitis comprises 12 centers from 8 United Network for Organ Sharing regions studying early liver transplantation (LT) (without mandated period of sobriety) for patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis (AH). We analyzed the outcomes of these patients.
Methods: We performed a retrospective study of consecutive patients with a diagnosis of severe AH and no prior diagnosis of liver disease or episodes of AH, who underwent LT before 6 months of abstinence from 2006 through 2017 at 12 centers. We collected data on baseline characteristics, psychosocial profiles, level of alcohol consumption before LT, disease course and treatment, and outcomes of LT. The interval of alcohol abstinence was defined as the time between last drink and the date of LT. The primary outcomes were survival and alcohol use after LT, defined as slip or sustained.
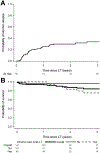
Results: Among 147 patients with AH who received liver transplants, the median duration of abstinence before LT was 55 days; 54% received corticosteroids for AH and the patients had a median Lille score of 0.82 and a median Sodium Model for End-Stage Liver Disease score of 39. Cumulative patient survival percentages after LT were 94% at 1 year (95% confidence interval [CI], 89%-97%) and 84% at 3 years (95% CI, 75%-90%). Following hospital discharge after LT, 72% were abstinent, 18% had slips, and 11% had sustained alcohol use. The cumulative incidence of any alcohol use was 25% at 1 year (95% CI, 18%-34%) and 34% at 3 years (95% CI, 25%-44%) after LT. The cumulative incidence of sustained alcohol use was 10% at 1 year (95% CI, 6%-18%) and 17% at 3 years (95% CI, 10%-27%) after LT. In multivariable analysis, only younger age was associated with alcohol following LT (P = .01). Sustained alcohol use after LT was associated with increased risk of death (hazard ratio, 4.59; P = .01).
Conclusions: In a retrospective analysis of 147 patients who underwent early LT (before 6 months of abstinence) for severe AH, we found that most patients survive for 1 year (94%) and 3 years (84%), similar to patients receiving liver transplants for other indications. Sustained alcohol use after LT was infrequent but associated with increased mortality. Our findings support the selective use of LT as a treatment for severe AH. Prospective studies are needed to optimize selection criteria, management of patients after LT, and long-term outcomes.
Keywords: 6 Months; ACCELERATE-AH; Recidivism; Relapse; UNOS.
Copyright © 2018 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures
Comment in
-
Early Liver Transplantation for Alcoholic Hepatitis.Gastroenterology. 2019 Jan;156(1):284-285. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.06.096. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30315772 No abstract available.
-
Outcomes After Early Liver Transplantation for Patients With Severe Alcoholic Hepatitis: Additional Evidence From a Meta-analysis.Gastroenterology. 2019 Jan;156(1):285-286. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.09.057. Epub 2018 Oct 10. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30315775 No abstract available.
-
Reply.Gastroenterology. 2019 Jan;156(1):286-287. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.11.044. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Gastroenterology. 2019. PMID: 30472234 No abstract available.
References
-
- Yang AL, Vadhavkar S, Singh G, et al. Epidemiology of alcohol-related liver and pancreatic disease in the United States. Arch Intern Med 2008;168:649–656. - PubMed
-
- O’Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ. Alcoholic liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:14–32. - PubMed
-
- Mathurin P Corticosteroids for alcoholic hepatitis— what’s next? J Hepatol 2005;43:526–533. - PubMed
-
- Louvet A, Naveau S, Abdelnour M, et al. The Lille model: a new tool for therapeutic strategy in patients with severe alcoholic hepatitis treated with steroids. Hepatology 2007;45:1348–1354. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

