Minimally Invasive Spinal Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity
- PMID: 29656622
- PMCID: PMC5944633
- DOI: 10.14245/ns.1836022.011
Minimally Invasive Spinal Surgery for Adult Spinal Deformity
Abstract
The purpose of this review is to present the current techniques and outcomes of adult spine deformity (ASD) surgery using the minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) approach. We performed a systemic search of PubMed for literature published through January 2018 with the following terms: "minimally invasive spine surgery," "adult spinal deformity," and "degenerative scoliosis." Of the 138 items that were found through this search, 57 English-language articles were selected for full-text review. According to the severity of the deformity and the symptoms, various types of MISS have been utilized, such as MISS decompression, circumferential MISS, and hybrid surgery. With proper indications, the MISS approach achieved satisfactory clinical and radiological outcomes for ASD, with reduced complication rates. Future studies should aim to define clear indications for the application of various surgical options.
Keywords: Adult spinal deformity; Degenerative scoliosis; Minimally invasive spine surgery.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures
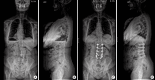
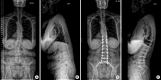
References
-
- Mummaneni PV, Shaffrey CI, Lenke LG, et al. The minimally invasive spinal deformity surgery algorithm: a reproducible rational framework for decision making in minimally invasive spinal deformity surgery. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36:E6. - PubMed
-
- Kanter AS, Tempel ZJ, Ozpinar A, et al. A review of minimally invasive procedures for the treatment of adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2016;41 Suppl 8:S59–65. - PubMed
-
- Anand N, Kong C, Fessler RG. A staged protocol for circumferential minimally invasive surgical correction of adult spinal deformity. Neurosurgery. 2017;81:733–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

