Direct Experimental Characterization of Glycosyl Cations by Infrared Ion Spectroscopy
- PMID: 29656643
- PMCID: PMC5958338
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.8b01236
Direct Experimental Characterization of Glycosyl Cations by Infrared Ion Spectroscopy
Abstract
Glycosyl cations are crucial intermediates formed during enzymatic and chemical glycosylation. The intrinsic high reactivity and short lifetime of these reaction intermediates make them very challenging to characterize using spectroscopic techniques. Herein, we report the use of collision induced dissociation tandem mass spectrometry to generate glycosyl cations in the gas phase followed by infrared ion spectroscopy using the FELIX infrared free electron laser. The experimentally observed IR spectra were compared to DFT calculated spectra enabling the detailed structural elucidation of elusive glycosyl oxocarbenium and dioxolenium ions.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

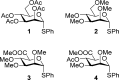

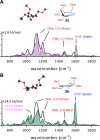

References
-
- Horenstein N. A. In Advances in Physical Organic Chemistry; Richard J. P., Ed.; Elsevier: New York, 2006; Vol. 41, p 275.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

