Exploring vitamin D metabolism and function in cancer
- PMID: 29657326
- PMCID: PMC5938036
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-018-0038-9
Exploring vitamin D metabolism and function in cancer
Abstract
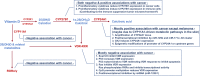
Vitamin D, traditionally known as an essential nutrient, is a precursor of a potent steroid hormone that regulates a broad spectrum of physiological processes. In addition to its classical roles in bone metabolism, epidemiological, preclinical, and cellular research during the last decades, it revealed that vitamin D may play a key role in the prevention and treatment of many extra-skeletal diseases such as cancer. Vitamin D, as a prohormone, undergoes two-step metabolism in liver and kidney to produce a biologically active metabolite, calcitriol, which binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) for the regulation of expression of diverse genes. In addition, recent studies have revealed that vitamin D can also be metabolized and activated through a CYP11A1-driven non-canonical metabolic pathway. Numerous anticancer properties of vitamin D have been proposed, with diverse effects on cancer development and progression. However, accumulating data suggest that the metabolism and functions of vitamin D are dysregulated in many types of cancer, conferring resistance to the antitumorigenic effects of vitamin D and thereby contributing to the development and progression of cancer. Thus, understanding dysregulated vitamin D metabolism and function in cancer will be critical for the development of promising new strategies for successful vitamin D-based cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Holick MF. Sunlight and vitamin D for bone health and prevention of autoimmune diseases, cancers, and cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004;80:1678S–1688S. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical