Top 50 Highly Cited Articles on Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) in Abdominal Radiology: A Bibliometric Analysis
- PMID: 29657641
- PMCID: PMC5894048
- DOI: 10.12659/PJR.904075
Top 50 Highly Cited Articles on Dual Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) in Abdominal Radiology: A Bibliometric Analysis
Abstract
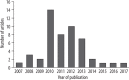
This study aims to identify the 50 most highly cited articles on dual energy computed tomography (DECT) in abdominal radiology Thomson Reuters Web of Science All Databases was queried without year or language restriction. Only original research articles with a primary focus on abdominal radiology using DECT were selected. Review articles, meta-analyses, and studies without human subjects were excluded. Fifty articles with the highest average yearly citation were identified. These articles were published between 2007 and 2017 in 12 journals, with the most in Radiology (12 articles). Articles had a median of 7 authors, with all first authors but one primarily affiliated to radiology departments. The United States of America produced the most articles (16), followed by Germany (13 articles), and China (7 articles). Most studies used Dual Source DECT technology (35 articles), followed by Rapid Kilovoltage Switching (14 articles), and Sequential Scanning (1 article). The top three scanned organs were the liver (24%), kidney (16%), and urinary tract (15%). The most commonly studied pathology was urinary calculi (28%), renal lesion/tumor (23%), and hepatic lesion/tumor (20%). Our study identifies intellectual milestones in the applications of DECT in abdominal radiology. The diversity of the articles reflects on the characteristics and quality of the most influential publications related to DECT.
Keywords: Abdomen; Bibliometrics; Tomography Scanners, X-Ray Computed.
Figures
References
-
- Lestra T, Mule S, Millet I, et al. Applications of dual energy computed tomography in abdominal imaging. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2016;97(6):593–603. - PubMed
-
- Mallinson PI, Coupal TM, McLaughlin PD, et al. Dual-Energy CT for the musculoskeletal system. Radiology. 2016;281:690–707. - PubMed
-
- Godin B. On the origins of bibliometrics. Scientometrics. 2006;68:109–33.
-
- Choudhri AF, Siddiqui A, Khan NR, Cohen HL. Understanding bibliometric parameters and analysis. Radiographics. 2015;35:736–46. - PubMed
-
- Abramo G, D’Angelo CA. Evaluating research: From informed peer review to bibliometrics. Scientometrics. 2011;87:499–514.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources