Inferring the Minimal Genome of Mesoplasma florum by Comparative Genomics and Transposon Mutagenesis
- PMID: 29657968
- PMCID: PMC5893858
- DOI: 10.1128/mSystems.00198-17
Inferring the Minimal Genome of Mesoplasma florum by Comparative Genomics and Transposon Mutagenesis
Abstract
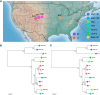
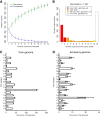
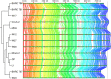
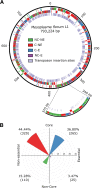
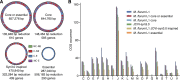
The creation and comparison of minimal genomes will help better define the most fundamental mechanisms supporting life. Mesoplasma florum is a near-minimal, fast-growing, nonpathogenic bacterium potentially amenable to genome reduction efforts. In a comparative genomic study of 13 M. florum strains, including 11 newly sequenced genomes, we have identified the core genome and open pangenome of this species. Our results show that all of the strains have approximately 80% of their gene content in common. Of the remaining 20%, 17% of the genes were found in multiple strains and 3% were unique to any given strain. On the basis of random transposon mutagenesis, we also estimated that ~290 out of 720 genes are essential for M. florum L1 in rich medium. We next evaluated different genome reduction scenarios for M. florum L1 by using gene conservation and essentiality data, as well as comparisons with the first working approximation of a minimal organism, Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn3.0. Our results suggest that 409 of the 473 M. mycoides JCVI-syn3.0 genes have orthologs in M. florum L1. Conversely, 57 putatively essential M. florum L1 genes have no homolog in M. mycoides JCVI-syn3.0. This suggests differences in minimal genome compositions, even for these evolutionarily closely related bacteria. IMPORTANCE The last years have witnessed the development of whole-genome cloning and transplantation methods and the complete synthesis of entire chromosomes. Recently, the first minimal cell, Mycoplasma mycoides JCVI-syn3.0, was created. Despite these milestone achievements, several questions remain to be answered. For example, is the composition of minimal genomes virtually identical in phylogenetically related species? On the basis of comparative genomics and transposon mutagenesis, we investigated this question by using an alternative model, Mesoplasma florum, that is also amenable to genome reduction efforts. Our results suggest that the creation of additional minimal genomes could help reveal different gene compositions and strategies that can support life, even within closely related species.
Keywords: Mesoplasma florum; comparative genomics; minimal genome; transposon mutagenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Hutchison CA III, Chuang RY, Noskov VN, Assad-Garcia N, Deerinck TJ, Ellisman MH, Gill J, Kannan K, Karas BJ, Ma L, Pelletier JF, Qi ZQ, Richter RA, Strychalski EA, Sun L, Suzuki Y, Tsvetanova B, Wise KS, Smith HO, Glass JI, Merryman C, Gibson DG, Venter JC. 2016. Design and synthesis of a minimal bacterial genome. Science 351:aad6253. doi: 10.1126/science.aad6253. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

