Development of 225Ac Radiopharmaceuticals: TRIUMF Perspectives and Experiences
- PMID: 29658444
- PMCID: PMC6249690
- DOI: 10.2174/1874471011666180416161908
Development of 225Ac Radiopharmaceuticals: TRIUMF Perspectives and Experiences
Abstract
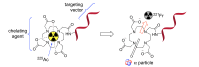
Background: The development of radiopharmaceuticals containing 225Ac for targeted alpha therapy is an active area of academic and commercial research worldwide.
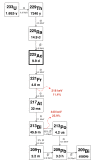
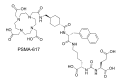
Objectives: Despite promising results from recent clinical trials, 225Ac-radiopharmaceutical development still faces significant challenges that must be overcome to realize the widespread clinical use of 225Ac. Some of these challenges include the limited availability of the isotope, the challenging chemistry required to isolate 225Ac from any co-produced isotopes, and the need for stable targeting systems with high radiolabeling yields.
Results: Here we provide a review of available literature pertaining to these challenges in the 225Acradiopharmaceutical field and also provide insight into how performed and planned efforts at TRIUMF - Canada's particle accelerator centre - aim to address these issues.
Keywords: Actinium-225; TRIUMF; isotope production; radiochemistry; radiolabeling; targeted alpha therapy..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures
References
-
- McDevitt M.R., Sgouros G., Finn R.D., Humm L.J., Jurcic J.G., Larson S.M., Scheinberg D.A. Radioimmunotherapy with alpha-emitting nuclides. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 1998;25(9):1341–1351. - PubMed
-
- Couturier O., Supiot S., Degraef-Mougin M., Faivre-Chauvet A., Car-lier T., Chatal J.F., Davodeau F., Cherel M. Cancer radioimmunotherapy with alpha-emitting nuclides. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2005;32(5):601–614. - PubMed
-
- Mulford D.A., Scheinberg D.A., Jurcic J.G. The promise of targeted {alpha}-particle therapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2005;46(1):S199–S204. - PubMed
-
- Wilbur S.D. Chemical and radiochemical considerations in radiolabeling with α-emitting radionuclides. Curr. Radiopharm. 2011;4:214–217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

