Vitamin D receptor suppresses proliferation and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma cell lines via regulating the expression of the epithelial Ca2+ channel TRPV5
- PMID: 29659618
- PMCID: PMC5901920
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195844
Vitamin D receptor suppresses proliferation and metastasis in renal cell carcinoma cell lines via regulating the expression of the epithelial Ca2+ channel TRPV5
Abstract
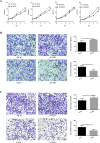
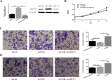
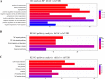
We previously demonstrated that transient receptor potential vanilloid subfamily 5 (TRPV5) expression was decreased in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) compared with that in normal kidney tissues, a finding that was correlated with vitamin D receptor (VDR) expression, but further investigations is warranted. The aim of this study was to elucidate whether VDR could regulate the expression of TRPV5 and affect proliferation and metastasis in RCC. In this study, we used lentivirus to conduct the model of VDR overexpression and knockdown caki-1 and 786-O RCC cell lines in vitro. The results demonstrated that VDR overexpression significantly inhibited RCC cells proliferation, migration and invasion, and promoted apoptosis by the MTT, transwell cell migration/invasion and flow cytometry assays, respectively. However, VDR knockdown in RCC cells had the opposite effect. The RNA-sequence assay, which was assessed in caki-1 cells after VDR overexpression and knockdown, also indicated that significantly differentially expressed genes were associated with cell apoptotic, differentiation, proliferation and migration. RT-PCR and western blot analysis showed that VDR knockdown increased TRPV5 expression and VDR overexpression decreased TRPV5 expression in caki-1 cells. Furthermore, knockdown of TRPV5 expression suppressed the VDR knockdown-induced change in the proliferation, migration and invasion in caki-1 cells. Taken together, these findings confirmed that VDR functions as a tumour suppressor in RCC cells and suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of RCC through regulating the expression of TRPV5.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


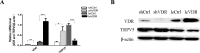
Similar articles
-
Decreased expression of the epithelial Ca2+ channel TRPV5 and TRPV6 in human renal cell carcinoma associated with vitamin D receptor.J Urol. 2011 Dec;186(6):2419-25. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2011.07.086. Epub 2011 Oct 21. J Urol. 2011. PMID: 22019165
-
MiR-125b promotes migration and invasion by targeting the vitamin D receptor in renal cell carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(1):150-156. doi: 10.7150/ijms.49328. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33390783 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-590-5p regulates cell viability, apoptosis, migration and invasion of renal cell carcinoma cell lines through targeting ARHGAP24.Mol Biosyst. 2017 Nov 21;13(12):2564-2573. doi: 10.1039/c7mb00406k. Mol Biosyst. 2017. PMID: 29019371
-
Jam3 promotes migration and suppresses apoptosis of renal carcinoma cell lines.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Nov;42(5):2923-2929. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3854. Epub 2018 Sep 4. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 30226554
-
miR‑205 suppresses cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis via regulation of the PTEN/AKT pathway in renal cell carcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Oct;14(4):3343-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5589. Epub 2016 Aug 4. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27498834
Cited by
-
JAK3 identified as a key toxicological target of aristolochic acid in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Mol Divers. 2025 Jun 30. doi: 10.1007/s11030-025-11268-6. Online ahead of print. Mol Divers. 2025. PMID: 40588582
-
Role of TRP channels in carcinogenesis and metastasis: Pathophysiology and regulation by non-coding RNAs.Noncoding RNA Res. 2023 Dec 18;9(2):359-366. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2023.12.001. eCollection 2024 Jun. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023. PMID: 38511066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KMT2D loss drives aggressive tumor phenotypes in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.Am J Cancer Res. 2022 Mar 15;12(3):1309-1322. eCollection 2022. Am J Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35411237 Free PMC article.
-
miR-103a-3p Silencing Ameliorates Calcium Oxalate Deposition in Rat Kidney by Activating the UMOD/TRPV5 Axis.Dis Markers. 2022 Feb 23;2022:2602717. doi: 10.1155/2022/2602717. eCollection 2022. Dis Markers. 2022. PMID: 35251369 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of TRPV family to prognosis and immune infiltration in renal clear cell carcinoma.Channels (Austin). 2022 Dec;16(1):84-96. doi: 10.1080/19336950.2022.2058733. Channels (Austin). 2022. PMID: 35389815 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sanchez-Gastaldo A, Kempf E, Gonzalez Del Alba A, Duran I. Systemic treatment of renal cell cancer: a comprehensive review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2017;60: 77–89. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2017.08.010 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68: 7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dutcher JP. Recent developments in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma. Ther Adv Urol. 2013;5: 338–353. doi: 10.1177/1756287213505672 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Joh HK, Giovannucci EL, Bertrand KA, Lim S, Cho E. Predicted plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D and risk of renal cell cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2013;105: 726–732. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djt082 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Muller DC, Fanidi A, Midttun O, Steffen A, Dossus L, Boutron-Ruault MC, et al. Circulating 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 in relation to renal cell carcinoma incidence and survival in the EPIC cohort. Am J Epidemiol. 2014;180: 810–820. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwu204 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

