Why do placentas evolve? Evidence for a morphological advantage during pregnancy in live-bearing fish
- PMID: 29659620
- PMCID: PMC5901924
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195976
Why do placentas evolve? Evidence for a morphological advantage during pregnancy in live-bearing fish
Abstract
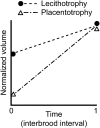
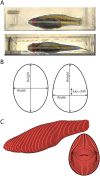
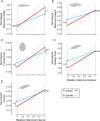
A live-bearing reproductive strategy can induce large morphological changes in the mother during pregnancy. The evolution of the placenta in swimming animals involves a shift in the timing of maternal provisioning from pre-fertilization (females supply their eggs with sufficient yolk reserves prior to fertilization) to post-fertilization (females provide all nutrients via a placenta during the pregnancy). It has been hypothesised that this shift, associated with the evolution of the placenta, should confer a morphological advantage to the females leading to a more slender body shape during the early stages of pregnancy. We tested this hypothesis by quantifying three-dimensional shape and volume changes during pregnancy and in full-grown virgin controls of two species within the live-bearing fish family Poeciliidae: Poeciliopsis gracilis (non-placental) and Poeciliopsis turneri (placental). We show that P. turneri is more slender than P. gracilis at the beginning of the interbrood interval and in virgins, and that these differences diminish towards the end of pregnancy. This study provides the first evidence for an adaptive morphological advantage of the placenta in live-bearing fish. A similar morphological benefit could drive the evolution of placentas in other live-bearing (swimming) animal lineages.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Mossman HW. Comparative morphogenesis of the fetal membranes and accessory uterine structures. Contrib Embryol. 1937;26: 129–246. - PubMed
-
- Wourms JP. Viviparity: the maternal-fetal relationships in fishes. Am Zool. 1981;21: 473–515.
-
- Wourms JP, Grove BD, Lombardi J. The maternal-embryonic relationship in viviparous fishes In: Hoar WS, Randal DJ, editors. Fish Physiology. New York: Academic Press; 1988. pp. 1–134.
-
- Wake MH. Evolutionary Scenarios, Homology and Convergence of Structural Specializations for Vertebrate Viviparity. Am Zool. 1992;32: 256–263.
-
- Blackburn DG. Evolution of vertebrate viviparity and specializations for fetal nutrition: A quantitative and qualitative analysis. J Morphol. 2015;276: 961–990. doi: 10.1002/jmor.20272 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

