Gut Barrier Dysfunction-A Primary Defect in Twins with Crohn's Disease Predominantly Caused by Genetic Predisposition
- PMID: 29659773
- PMCID: PMC6225972
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy045
Gut Barrier Dysfunction-A Primary Defect in Twins with Crohn's Disease Predominantly Caused by Genetic Predisposition
Erratum in
-
Correction.J Crohns Colitis. 2023 Jan 27;17(1):149. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac104. J Crohns Colitis. 2023. PMID: 35971821 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and aims: The aetiology of Crohn's disease is poorly understood. By investigating twin pairs discordant for Crohn's disease, we aimed to assess whether the dysregulated barrier represents a cause or a consequence of inflammation and to evaluate the impact of genetic predisposition on barrier function.
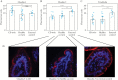
Methods: Ileal biopsies from 15 twin pairs discordant for Crohn's disease [monozygotic n = 9, dizygotic n = 6] and 10 external controls were mounted in Ussing chambers to assess paracellular permeability to 51Chromium [Cr]-EDTA and trancellular passage to non-pathogenic E. coli K-12. Experiments were performed with and without provocation with acetylsalicylic acid. Immunofluorescence and ELISA were used to quantify the expression level of tight junction proteins.
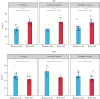
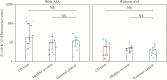
Results: Healthy co-twins and affected twins displayed increased 51Cr-EDTA permeability at 120 min, both with acetylsalicylic acid [p < 0.001] and without [p < 0.001] when compared with controls. A significant increase in 51Cr-EDTA flux was already seen at 20 min in healthy monozygotic co-twins compared with controls [p≤0.05] when stratified by zygosity, but not in healthy dizygotic co-twins. No difference in E. coli passage was observed between groups. Immunofluorescence of the tight junction proteins claudin-5 and tricellulin showed lower levels in healthy co-twins [p < 0.05] and affected twins [p < 0.05] compared with external controls, while ELISA only showed lower tricellulin in Crohn's disease twins [p < 0.05].
Conclusion: Our results suggest that barrier dysfunction is a primary defect in Crohn's disease, since changes were predominantly seen in healthy monozygotic co-twins. Passage of E. coli seems to be a consequence of inflammation, rather than representing a primary defect.
Figures


Comment in
-
Letter to the Editor.J Crohns Colitis. 2022 Nov 23;16(11):1792-1793. doi: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab225. J Crohns Colitis. 2022. PMID: 35073577 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ananthakrishnan AN. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;12:205–17. - PubMed
-
- Bjarnason I, O’Morain C, Levi AJ, Peters TJ. Absorption of 51chromium-labeled ethylenediaminetetraacetate in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 1983;85:318–22. - PubMed
-
- Barmeyer C, Fromm M, Schulzke JD. Active and passive involvement of claudins in the pathophysiology of intestinal inflammatory diseases. Pflugers Arch 2017;469:15–26. - PubMed
-
- Keita AV, Salim SY, Jiang T, et al. . Increased uptake of non-pathogenic E. coli via the follicle-associated epithelium in longstanding ileal Crohn’s disease. J Pathol 2008;215:135–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

