Clinically Actionable Hypercholesterolemia and Hypertriglyceridemia in Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- PMID: 29661561
- PMCID: PMC6019181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2018.02.038
Clinically Actionable Hypercholesterolemia and Hypertriglyceridemia in Children with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Abstract
Objective: To determine the percentage of children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in whom intervention for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol or triglycerides was indicated based on National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute guidelines.
Study design: This multicenter, longitudinal cohort study included children with NAFLD enrolled in the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network. Fasting lipid profiles were obtained at diagnosis. Standardized dietary recommendations were provided. After 1 year, lipid profiles were repeated and interpreted according to National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction. Main outcomes were meeting criteria for clinically actionable dyslipidemia at baseline, and either achieving lipid goal at follow-up or meeting criteria for ongoing intervention.
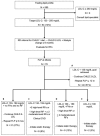
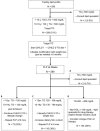
Results: There were 585 participants, with a mean age of 12.8 years. The prevalence of children warranting intervention for low-density lipoprotein cholesterol at baseline was 14%. After 1 year of recommended dietary changes, 51% achieved goal low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, 27% qualified for enhanced dietary and lifestyle modifications, and 22% met criteria for pharmacologic intervention. Elevated triglycerides were more prevalent, with 51% meeting criteria for intervention. At 1 year, 25% achieved goal triglycerides with diet and lifestyle changes, 38% met criteria for advanced dietary modifications, and 37% qualified for antihyperlipidemic medications.
Conclusions: More than one-half of children with NAFLD met intervention thresholds for dyslipidemia. Based on the burden of clinically relevant dyslipidemia, lipid screening in children with NAFLD is warranted. Clinicians caring for children with NAFLD should be familiar with lipid management.
Keywords: NAFLD; cardiovascular; diet; dyslipidemia; pediatric; statin.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Heart Disease Facts & Statistics [Internet] [accessed March 9, 2017];The Center for Disease Control. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/heartdisease/facts.htm.
-
- Newman W, Freedman D, Voors A, Gard P, Srinivasan S, Cresanta J, Williamson G, et al. Relation of Serum Lipoprotein Levels and Systolic Blood Pressure to Early Atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med. 1986;314:138–144. - PubMed
-
- McGill HC, McMahan CA. Determinants of atherosclerosis in the young. Pathobiological Determinants of Atherosclerosis in Youth (PDAY) Research Group. Am J Cardiol. 1998;82:30T–36T. - PubMed
-
- Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Expert Panel on Integrated Guidelines for Cardiovascular Health and Risk Reduction in Children and Adolescents: Summary Report. Pediatrics. 2011;128:S213–S256. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schwimmer JB, Deutsch R, Kahen T, Lavine JE, Stanley C, Behling C. Prevalence of fatty liver in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2006;118:1388–1393. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK061731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK078392/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000006/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001422/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061730/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061728/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000439/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000454/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K08 DK098623/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000077/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- TL1 TR001107/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061737/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061713/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061732/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000150/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061718/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001442/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061738/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002378/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001425/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002319/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000423/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000100/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

