The role of beta cell heterogeneity in islet function and insulin release
- PMID: 29661799
- PMCID: PMC5976077
- DOI: 10.1530/JME-18-0011
The role of beta cell heterogeneity in islet function and insulin release
Abstract
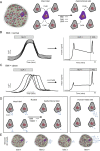
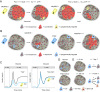
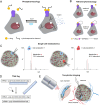
It is becoming increasingly apparent that not all insulin-secreting beta cells are equal. Subtle differences exist at the transcriptomic and protein expression levels, with repercussions for beta cell survival/proliferation, calcium signalling and insulin release. Notably, beta cell heterogeneity displays plasticity during development, metabolic stress and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Thus, heterogeneity or lack thereof may be an important contributor to beta cell failure during T2DM in both rodents and humans. The present review will discuss the molecular and cellular features of beta cell heterogeneity at both the single-cell and islet level, explore how this influences islet function and insulin release and look into the alterations that may occur during obesity and T2DM.
Keywords: diabetes II; insulin secretion; metabolism; pancreatic beta cell.
© 2018 The authors.
Figures
References
-
- Aichler M, Borgmann D, Krumsiek J, Buck A, MacDonald PE, Fox JEM, Lyon J, Light PE, Keipert S, Jastroch M, et al 2017. N-acyl taurines and acylcarnitines cause an imbalance in insulin synthesis and secretion provoking β cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metabolism 25 1334.e1334–1347.e1334. (10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.012) - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

