Interferon Independent Non-Canonical STAT Activation and Virus Induced Inflammation
- PMID: 29662014
- PMCID: PMC5923490
- DOI: 10.3390/v10040196
Interferon Independent Non-Canonical STAT Activation and Virus Induced Inflammation
Abstract
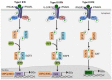
Interferons (IFNs) are a group of secreted proteins that play critical roles in antiviral immunity, antitumor activity, activation of cytotoxic T cells, and modulation of host immune responses. IFNs are cytokines, and bind receptors on cell surfaces to trigger signal transduction. The major signaling pathway activated by IFNs is the JAK/STAT (Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription) pathway, a complex pathway involved in both viral and host survival strategies. On the one hand, viruses have evolved strategies to escape from antiviral host defenses evoked by IFN-activated JAK/STAT signaling. On the other hand, viruses have also evolved to exploit the JAK/STAT pathway to evoke activation of certain STATs that somehow promote viral pathogenesis. In this review, recent progress in our understanding of the virus-induced IFN-independent STAT signaling and its potential roles in viral induced inflammation and pathogenesis are summarized in detail, and perspectives are provided.
Keywords: Interferons; JAK/STAT signaling; inflammation; non-canonical STAT activation; viral antagonism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical