Greenland records of aerosol source and atmospheric lifetime changes from the Eemian to the Holocene
- PMID: 29662058
- PMCID: PMC5902614
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03924-3
Greenland records of aerosol source and atmospheric lifetime changes from the Eemian to the Holocene
Abstract
The Northern Hemisphere experienced dramatic changes during the last glacial, featuring vast ice sheets and abrupt climate events, while high northern latitudes during the last interglacial (Eemian) were warmer than today. Here we use high-resolution aerosol records from the Greenland NEEM ice core to reconstruct the environmental alterations in aerosol source regions accompanying these changes. Separating source and transport effects, we find strongly reduced terrestrial biogenic emissions during glacial times reflecting net loss of vegetated area in North America. Rapid climate changes during the glacial have little effect on terrestrial biogenic aerosol emissions. A strong increase in terrestrial dust emissions during the coldest intervals indicates higher aridity and dust storm activity in East Asian deserts. Glacial sea salt aerosol emissions in the North Atlantic region increase only moderately (50%), likely due to sea ice expansion. Lower aerosol concentrations in Eemian ice compared to the Holocene are mainly due to shortened atmospheric residence time, while emissions changed little.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


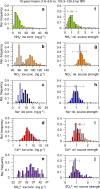
References
-
- Grootes PM, Stuiver M, White JWC, Johnsen S, Jouzel J. Comparison of oxygen isotope records from the GISP2 and GRIP Greenland ice cores. Nature. 1993;366:552–554. doi: 10.1038/366552a0. - DOI
-
- de Angelis M, Steffensen JP, Legrand M, Clausen H, Hammer C. Primary aerosol (sea salt and soil dust) deposited in Greenland ice during the last climatic cycle: comparison with east Antarctic records. J. Geophys. Res. 1997;102:26681–26698. doi: 10.1029/97JC01298. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

