Pharmacodynamics of mutant-IDH1 inhibitors in glioma patients probed by in vivo 3D MRS imaging of 2-hydroxyglutarate
- PMID: 29662077
- PMCID: PMC5902553
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-018-03905-6
Pharmacodynamics of mutant-IDH1 inhibitors in glioma patients probed by in vivo 3D MRS imaging of 2-hydroxyglutarate
Abstract
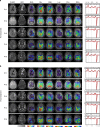
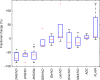
Inhibitors of the mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) entered recently in clinical trials for glioma treatment. Mutant IDH1 produces high levels of 2-hydroxyglurate (2HG), thought to initiate oncogenesis through epigenetic modifications of gene expression. In this study, we show the initial evidence of the pharmacodynamics of a new mutant IDH1 inhibitor in glioma patients, using non-invasive 3D MR spectroscopic imaging of 2HG. Our results from a Phase 1 clinical trial indicate a rapid decrease of 2HG levels by 70% (CI 13%, P = 0.019) after 1 week of treatment. Importantly, inhibition of mutant IDH1 may lead to the reprogramming of tumor metabolism, suggested by simultaneous changes in glutathione, glutamine, glutamate, and lactate. An inverse correlation between metabolic changes and diffusion MRI indicates an effect on the tumor-cell density. We demonstrate a feasible radiopharmacodynamics approach to support the rapid clinical translation of rationally designed drugs targeting IDH1/2 mutations for personalized and precision medicine of glioma patients.
Conflict of interest statement
T.T.B. received consulting honoraria from Merck & Co., Roche, Kirin Pharmaceuticals, Spectrum, Amgen, and Novartis. The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

