The cytoplasmic dynein transport machinery and its many cargoes
- PMID: 29662141
- PMCID: PMC6457270
- DOI: 10.1038/s41580-018-0004-3
The cytoplasmic dynein transport machinery and its many cargoes
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: The cytoplasmic dynein transport machinery and its many cargoes.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Jul;19(7):479. doi: 10.1038/s41580-018-0021-2. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29740130
Abstract
Cytoplasmic dynein 1 is an important microtubule-based motor in many eukaryotic cells. Dynein has critical roles both in interphase and during cell division. Here, we focus on interphase cargoes of dynein, which include membrane-bound organelles, RNAs, protein complexes and viruses. A central challenge in the field is to understand how a single motor can transport such a diverse array of cargoes and how this process is regulated. The molecular basis by which each cargo is linked to dynein and its cofactor dynactin has started to emerge. Of particular importance for this process is a set of coiled-coil proteins - activating adaptors - that both recruit dynein-dynactin to their cargoes and activate dynein motility.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures
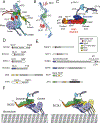
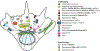
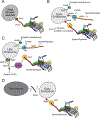
References
-
-
Gibbons IR & Rowe AJ Dynein: A Protein with Adenosine Triphosphatase Activity from Cilia. Science 149, 424–6 (1965).
Describes the original discovey of dynein.
-
-
-
Paschal BM, Shpetner HS & Vallee RB MAP 1C is a microtubule-activated ATPase which translocates microtubules in vitro and has dynein-like properties. J Cell Biol 105, 1273–82 (1987).
Describes the discovery of cytoplasmic dynein-1.
-
-
-
Paschal BM & Vallee RB Retrograde transport by the microtubule-associated protein MAP 1C. Nature 330, 181–3 (1987).
Shows that cytoplasmic dynein-1 is a minus-end-directed motor.
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

