Locomotor activity modulates associative learning in mouse cerebellum
- PMID: 29662214
- PMCID: PMC5923878
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-018-0129-x
Locomotor activity modulates associative learning in mouse cerebellum
Abstract
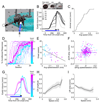
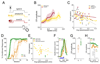
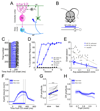
Changes in behavioral state can profoundly influence brain function. Here we show that behavioral state modulates performance in delay eyeblink conditioning, a cerebellum-dependent form of associative learning. Increased locomotor speed in head-fixed mice drove earlier onset of learning and trial-by-trial enhancement of learned responses that were dissociable from changes in arousal and independent of sensory modality. Eyelid responses evoked by optogenetic stimulation of mossy fiber inputs to the cerebellum, but not at sites downstream, were positively modulated by ongoing locomotion. Substituting prolonged, low-intensity optogenetic mossy fiber stimulation for locomotion was sufficient to enhance conditioned responses. Our results suggest that locomotor activity modulates delay eyeblink conditioning through increased activation of the mossy fiber pathway within the cerebellum. Taken together, these results provide evidence for a novel role for behavioral state modulation in associative learning and suggest a potential mechanism through which engaging in movement can improve an individual's ability to learn.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
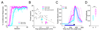
Comment in
-
Yet another reason to walk instead of drive.Nat Neurosci. 2018 May;21(5):648-649. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0142-0. Nat Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29662212 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

