Hepatitis B virus pre-S/S variants in liver diseases
- PMID: 29662289
- PMCID: PMC5897855
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i14.1507
Hepatitis B virus pre-S/S variants in liver diseases
Abstract
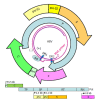
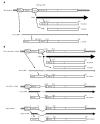
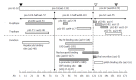
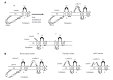
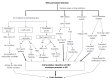
Chronic hepatitis B is a global health problem. The clinical outcomes of chronic hepatitis B infection include asymptomatic carrier state, chronic hepatitis (CH), liver cirrhosis (LC), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Because of the spontaneous error rate inherent to viral reverse transcriptase, the hepatitis B virus (HBV) genome evolves during the course of infection under the antiviral pressure of host immunity. The clinical significance of pre-S/S variants has become increasingly recognized in patients with chronic HBV infection. Pre-S/S variants are often identified in hepatitis B carriers with CH, LC, and HCC, which suggests that these naturally occurring pre-S/S variants may contribute to the development of progressive liver damage and hepatocarcinogenesis. This paper reviews the function of the pre-S/S region along with recent findings related to the role of pre-S/S variants in liver diseases. According to the mutation type, five pre-S/S variants have been identified: pre-S deletion, pre-S point mutation, pre-S1 splice variant, C-terminus S point mutation, and pre-S/S nonsense mutation. Their associations with HBV genotype and the possible pathogenesis of pre-S/S variants are discussed. Different pre-S/S variants cause liver diseases through different mechanisms. Most cause the intracellular retention of HBV envelope proteins and induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress, which results in liver diseases. Pre-S/S variants should be routinely determined in HBV carriers to help identify individuals who may be at a high risk of less favorable liver disease progression. Additional investigations are required to explore the molecular mechanisms of the pre-S/S variants involved in the pathogenesis of each stage of liver disease.
Keywords: Chronic hepatitis; Hepatitis B virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Liver cirrhosis; Pre-S deletion; Pre-S/S mutant; Splice variant; spPS1.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kao JH, Chen DS. Global control of hepatitis B virus infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2002;2:395–403. - PubMed
-
- Liu CJ, Kao JH. Global perspective on the natural history of chronic hepatitis B: role of hepatitis B virus genotypes A to J. Semin Liver Dis. 2013;33:97–102. - PubMed
-
- Lin CL, Kao JH. The clinical implications of hepatitis B virus genotype: Recent advances. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;26 Suppl 1:123–130. - PubMed
-
- Sugauchi F, Ohno T, Orito E, Sakugawa H, Ichida T, Komatsu M, Kuramitsu T, Ueda R, Miyakawa Y, Mizokami M. Influence of hepatitis B virus genotypes on the development of preS deletions and advanced liver disease. J Med Virol. 2003;70:537–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

