Distribution and determinants of pneumonia diagnosis using Integrated Management of Childhood Illness guidelines: a nationally representative study in Malawi
- PMID: 29662688
- PMCID: PMC5898357
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjgh-2017-000506
Distribution and determinants of pneumonia diagnosis using Integrated Management of Childhood Illness guidelines: a nationally representative study in Malawi
Erratum in
-
Correction: Distribution and determinants of pneumonia diagnosis using integrated management of childhood illness guidelines: a nationally representative study in Malawi.BMJ Glob Health. 2018 Jun 15;3(3):e000506corr1. doi: 10.1136/bmjgh-2017-000506corr1. eCollection 2018. BMJ Glob Health. 2018. PMID: 29946490 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Pneumonia remains the leading cause of child mortality in sub-Saharan Africa. The Integrated Management of Childhood Illness (IMCI) strategy was developed to standardise care in low-income and middle-income countries for major childhood illnesses and can effectively improve healthcare worker performance. Suboptimal clinical evaluation can result in missed diagnoses and excess morbidity and mortality. We estimate the sensitivity of pneumonia diagnosis and investigate its determinants among children in Malawi.
Methods: Data were obtained from the 2013-2014 Service Provision Assessment survey, a census of health facilities in Malawi that included direct observation of care and re-examination of children by trained observers. We calculated sensitivity of pneumonia diagnosis and used multilevel log-binomial regression to assess factors associated with diagnostic sensitivity.
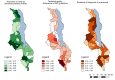
Results: 3136 clinical visits for children 2-59 months old were observed at 742 health facilities. Healthcare workers completed an average of 30% (SD 13%) of IMCI guidelines in each encounter. 573 children met the IMCI criteria for pneumonia; 118 (21%) were correctly diagnosed. Advanced practice clinicians were more likely than other providers to diagnose pneumonia correctly (adjusted relative risk 2.00, 95% CI 1.21 to 3.29). Clinical quality was strongly associated with correct diagnosis: sensitivity was 23% in providers at the 75th percentile for guideline adherence compared with 14% for those at the 25th percentile. Contextual factors, facility structural readiness, and training or supervision were not associated with sensitivity.
Conclusions: Care quality for Malawian children is poor, with low guideline adherence and missed diagnosis for four of five children with pneumonia. Better sensitivity is associated with provider type and higher adherence to IMCI. Existing interventions such as training and supportive supervision are associated with higher guideline adherence, but are insufficient to meaningfully improve sensitivity. Innovative and scalable quality improvement interventions are needed to strengthen health systems and reduce avoidable child mortality.
Keywords: child health; cross-sectional survey; health systems; pneumonia.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Towards a grand convergence for child survival and health: a strategic review of options for the future building on lessons learnt from IMNCI. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2016.
-
- World Health Organization. The United Nations Children’s Fund. Ending preventable child deaths from pneumonia and diarrhea by 2025: the integrated Global Action Plan for Pneumonia and Diarrhoea (GAPPD). Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2013.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous