Progression of MDS-UPDRS Scores Over Five Years in De Novo Parkinson Disease from the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative Cohort
- PMID: 29662921
- PMCID: PMC5898442
- DOI: 10.1002/mdc3.12553
Progression of MDS-UPDRS Scores Over Five Years in De Novo Parkinson Disease from the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative Cohort
Abstract
Background: The Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UDPRS) is a commonly used tool to measure Parkinson disease (PD) progression. Longitudinal changes in MDS-UPDRS scores in de novo PD have not been established.
Objective: Determine progression rates of MDS-UPDRS scores in de novo PD.
Methods: 362 participants from the Parkinson's Progression Markers Initiative, a multicenter longitudinal cohort study of de novo PD, were included. Longitudinal progression of MDS-UPDRS total and subscale scores were modeled using mixed model regression.
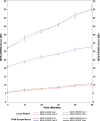
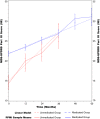
Results: MDS-UPDRS scores increased in a linear fashion over five years in de novo PD. MDS-UPDRS total score increased an estimated 4.0 points/year, Part I 0.25 points/year, Part II 1.0 points/year, and Part III 2.4 points/year.
Conclusions: The expected average progression of MDS-UPDRS scores in de novo PD from this study can assist in clinical monitoring and provide comparative data for detection of disease modification in treatment trials.
Keywords: MDS-UPDRS; Parkinson disease; biomarkers; disease progression.
Figures
References
-
- Ramaker C, Marinus J, Stiggelbout AM, Van Hilten BJ. Systematic evaluation of rating scales for impairment and disability in Parkinson's disease. Mov Disord 2002;17:867–876. - PubMed
-
- Martinez‐Martin P, Gil‐Nagel A, Gracia LM, Gomez JB, Martinez‐Sarries J, Bermejo F. Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale characteristics and structure. The Cooperative Multicentric Group. Mov Disord 1994;9:76–83. - PubMed
-
- Rabey JM, Bass H, Bonuccelli U, et al. Evaluation of the Short Parkinson's Evaluation Scale: a new friendly scale for the evaluation of Parkinson's disease in clinical drug trials. Clin Neuropharmacol 1997;20:322–337. - PubMed
-
- Stebbins GT, Goetz CG, Lang AE, Cubo E. Factor analysis of the motor section of the Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale during the off‐state. Mov Disord 1999;14:585–589. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

