Worldwide assessment of healthcare personnel dealing with lymphoedema
- PMID: 29663122
- PMCID: PMC5901432
- DOI: 10.1186/s13561-018-0194-6
Worldwide assessment of healthcare personnel dealing with lymphoedema
Abstract
Background: Lymphoedema is a pandemic with about 250 million people suffering from this condition worldwide. Lymphatic diseases have considerable public health significance, but yet few professionals are specialised in their management causing a substantial burden on health resources.
Aims and objectives: This study aims to give an overview of the approximate number of medical professionals, professional societies, institutions and companies dealing with lymphoedema in various countries. Concepts of improvement for current human resources are considered.
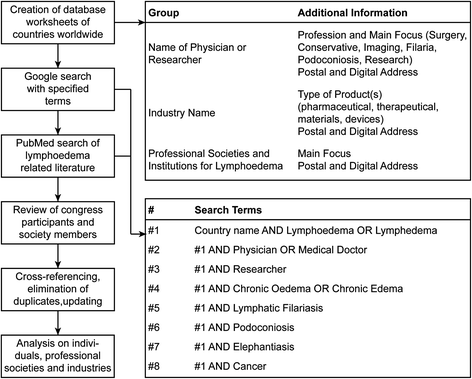
Methods: An online database analysis (Google search engine and PubMed) was carried out for each country of the world. Additionally, relevant congress participant lists as well as member lists of significant medical societies and reports of the World Health Organisation were analysed.
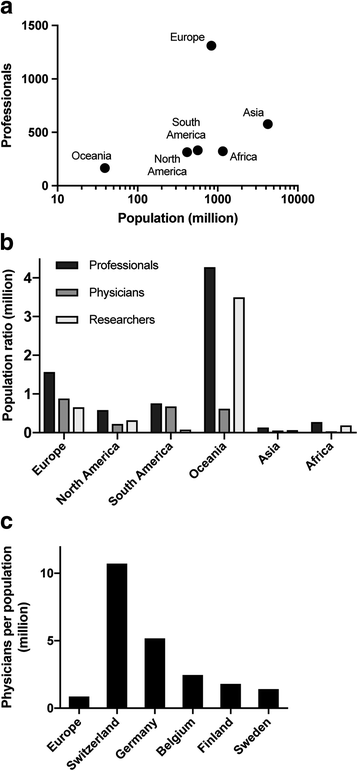
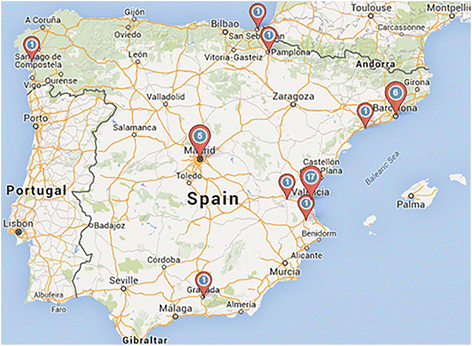
Results: Overall distribution of tertiary level professionals specialised in this field is heterogenous. A decrescent gradient of professionals can be seen between developed and developing countries and between urban and rural areas. Countries in general do not seem to have yet met the current demand for specialists at tertiary level in this field.
Conclusions: This study intends to draw attention to the current medical coverage gaps due to a low number of lymphoedema specialists at tertiary level. It wishes to start a discussion about structured reimbursement and certification of knowledge and skills that are essential incentives for experts to act as multiplicators and change the lack of care in the mid-term. Current fail prescriptions and evitable disability and sick certificates represent a high financial burden that could be reinvested in a correct management. Policy makers must focus in the two above mentioned essential measures. Medical training and the consequent development of the industry will then naturally take place, as it was the case for other professional groups in the past.
Keywords: Lymphatic diseases; Lymphoedema; Lymphology; Medical education; Medical healthcare resources.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Competing interests
We confirm that this manuscript describes original work and has neither been published elsewhere nor is under consideration by any other journal. All authors have approved the manuscript and agree with its submission to Health Economics Review. The study authors have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Földi M, Földi E. Földi’s textbook of lymphology for physicians and Lymphoedema therapists. 3rd rev. München: Urban & Fischer; 2012.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

