Older Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders in Sweden: A Register Study of Diagnoses, Psychiatric Care Utilization and Psychotropic Medication of 601 Individuals
- PMID: 29663191
- PMCID: PMC6096790
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-018-3567-0
Older Adults with Autism Spectrum Disorders in Sweden: A Register Study of Diagnoses, Psychiatric Care Utilization and Psychotropic Medication of 601 Individuals
Abstract
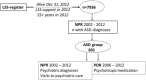
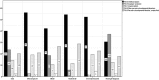
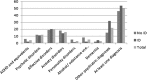
In a Swedish sample of persons eligible for disability services and aged 55 years or older in 2012, persons (n = 601) with autism spectrum disorder diagnoses registered in specialist care were identified. Register data concerning diagnoses of other psychiatric disorders, psychiatric care, and psychiatric medication were reviewed. More than 60% had been in contact with psychiatric care. The majority had no intellectual disability (ID) diagnosis recorded during the study period. Apart from ID, affective disorders, anxiety and psychotic disorders were most commonly registered; alcohol/substance abuse disorders were uncommon. Psychotropic drug prescriptions were very common, especially in the ID group. Professionals need awareness of this vulnerable group; studies concerning their life circumstances and service requirements should be conducted.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorders; Older adults; Psychiatry.
Figures
References
-
- Act concerning Support and Service for Persons with Certain Functional Impairments. (1993). In: Swedish: Lag om stöd och service till vissa funktionshindrade (LSS), p. 387.
-
- Åkerström B. Adults with autism and mental retardation. A life-span perspective. Uppsala: Uppsala University; 2001.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 4. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical