Empirical Comparison of Publication Bias Tests in Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 29663281
- PMCID: PMC6082203
- DOI: 10.1007/s11606-018-4425-7
Empirical Comparison of Publication Bias Tests in Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Decision makers rely on meta-analytic estimates to trade off benefits and harms. Publication bias impairs the validity and generalizability of such estimates. The performance of various statistical tests for publication bias has been largely compared using simulation studies and has not been systematically evaluated in empirical data.
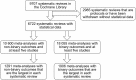
Methods: This study compares seven commonly used publication bias tests (i.e., Begg's rank test, trim-and-fill, Egger's, Tang's, Macaskill's, Deeks', and Peters' regression tests) based on 28,655 meta-analyses available in the Cochrane Library.
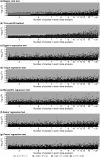
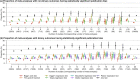
Results: Egger's regression test detected publication bias more frequently than other tests (15.7% in meta-analyses of binary outcomes and 13.5% in meta-analyses of non-binary outcomes). The proportion of statistically significant publication bias tests was greater for larger meta-analyses, especially for Begg's rank test and the trim-and-fill method. The agreement among Tang's, Macaskill's, Deeks', and Peters' regression tests for binary outcomes was moderately strong (most κ's were around 0.6). Tang's and Deeks' tests had fairly similar performance (κ > 0.9). The agreement among Begg's rank test, the trim-and-fill method, and Egger's regression test was weak or moderate (κ < 0.5).
Conclusions: Given the relatively low agreement between many publication bias tests, meta-analysts should not rely on a single test and may apply multiple tests with various assumptions. Non-statistical approaches to evaluating publication bias (e.g., searching clinical trials registries, records of drug approving agencies, and scientific conference proceedings) remain essential.
Keywords: Cochrane Library; funnel plot; meta-analysis; publication bias; statistical test.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have a conflict of interest.
Figures

Comment in
-
Capsule Commentary on Lin et. al. Empirical Comparison of Publication Bias Tests in Meta-analysis.J Gen Intern Med. 2018 Aug;33(8):1382. doi: 10.1007/s11606-018-4528-1. J Gen Intern Med. 2018. PMID: 29948811 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Begg CB, Berlin JA. Publication bias: a problem in interpreting medical data. J R Stat Soc Ser A (Stat Soc). 1988;151(3):419–63. doi: 10.2307/2982993. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

