On the role of extrinsic noise in microRNA-mediated bimodal gene expression
- PMID: 29664903
- PMCID: PMC5922620
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1006063
On the role of extrinsic noise in microRNA-mediated bimodal gene expression
Abstract
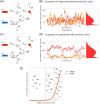
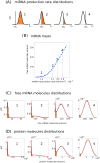
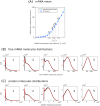
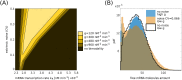
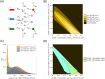
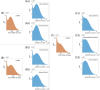
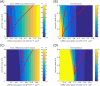
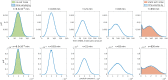
Several studies highlighted the relevance of extrinsic noise in shaping cell decision making and differentiation in molecular networks. Bimodal distributions of gene expression levels provide experimental evidence of phenotypic differentiation, where the modes of the distribution often correspond to different physiological states of the system. We theoretically address the presence of bimodal phenotypes in the context of microRNA (miRNA)-mediated regulation. MiRNAs are small noncoding RNA molecules that downregulate the expression of their target mRNAs. The nature of this interaction is titrative and induces a threshold effect: below a given target transcription rate almost no mRNAs are free and available for translation. We investigate the effect of extrinsic noise on the system by introducing a fluctuating miRNA-transcription rate. We find that the presence of extrinsic noise favours the presence of bimodal target distributions which can be observed for a wider range of parameters compared to the case with intrinsic noise only and for lower miRNA-target interaction strength. Our results suggest that combining threshold-inducing interactions with extrinsic noise provides a simple and robust mechanism for obtaining bimodal populations without requiring fine tuning. Furthermore, we characterise the protein distribution's dependence on protein half-life.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of microRNA-mediated negative feedback on gene expression noise.Biophys J. 2023 Nov 7;122(21):4220-4240. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.09.019. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37803829 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs confer phenotypic robustness to gene networks by suppressing biological noise.Nat Commun. 2013;4:2364. doi: 10.1038/ncomms3364. Nat Commun. 2013. PMID: 24077216 Free PMC article.
-
On the attenuation and amplification of molecular noise in genetic regulatory networks.BMC Bioinformatics. 2006 Feb 2;7:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-52. BMC Bioinformatics. 2006. PMID: 16457708 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and consequences of miRNA-target interactions--beyond repression of gene expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 Sep;15(9):599-612. doi: 10.1038/nrg3765. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 25022902 Review.
-
Functional aspects of animal microRNAs.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008 Feb;65(4):545-62. doi: 10.1007/s00018-007-7355-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2008. PMID: 17965831 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of microRNA-mediated negative feedback on gene expression noise.Biophys J. 2023 Nov 7;122(21):4220-4240. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2023.09.019. Epub 2023 Oct 6. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 37803829 Free PMC article.
-
microRNA-mediated noise processing in cells: A fight or a game?Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020 Mar 10;18:642-649. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2020.02.020. eCollection 2020. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2020. PMID: 32257047 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stochastic sequestration dynamics: a minimal model with extrinsic noise for bimodal distributions and competitors correlation.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 10;8(1):10387. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28647-9. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29991682 Free PMC article.
-
Single-cell Transcriptomes Reveal Characteristics of MicroRNAs in Gene Expression Noise Reduction.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021 Jun;19(3):394-407. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2021.05.002. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34606979 Free PMC article.
-
Out-of-Equilibrium ceRNA Crosstalk.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2883:167-193. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4290-0_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39702709
References
-
- Bessarabova M, Kirillov E, Shi W, Bugrim A, Nikolsky Y, Nikolskaya T. Bimodal gene expression patterns in breast cancer. BMC Genomics. 2010;11(Suppl I): S8 doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-11-S1-S8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shalek AK, Satija R, Adiconis X, Gertner RS, Gaublomme JT, Raychowdhury R, et al. Single-cell transcriptomics reveals bimodality in expression and splicing in immune cells. Nature. 2013;498:236–240. doi: 10.1038/nature12172 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nikolsky Y, Kirillov E, Serebryiskaya T, Rakhmatulin R, Perlina A, Bugrim A, et al. Sequential clustering of breast cancers using bimodal gene expression. Proceed AACR Ann Meeting. 2007; p. 141.
-
- Dozmorov I, Knowlton N, Tang Y, Shields A, Pathipvanich P, Jarvis J, et al. Hypervariable genes–experimental error or hidden dynamics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32 (19):e147–10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gnh146 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao H, Yue P, Fang K. Identification of differentially expressed genes with multivariate outlier analysis. J Biopharm Stat. 2004;14 (3):629–646. doi: 10.1081/BIP-200025654 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

