Type I interferons in tuberculosis: Foe and occasionally friend
- PMID: 29666166
- PMCID: PMC5940272
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20180325
Type I interferons in tuberculosis: Foe and occasionally friend
Abstract
Tuberculosis remains one of the leading causes of mortality worldwide, and, despite its clinical significance, there are still significant gaps in our understanding of pathogenic and protective mechanisms triggered by Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Type I interferons (IFN) regulate a broad family of genes that either stimulate or inhibit immune function, having both host-protective and detrimental effects, and exhibit well-characterized antiviral activity. Transcriptional studies have uncovered a potential deleterious role for type I IFN in active tuberculosis. Since then, additional studies in human tuberculosis and experimental mouse models of M. tuberculosis infection support the concept that type I IFN promotes both bacterial expansion and disease pathogenesis. More recently, studies in a different setting have suggested a putative protective role for type I IFN. In this study, we discuss the mechanistic and contextual factors that determine the detrimental versus beneficial outcomes of type I IFN induction during M. tuberculosis infection, from human disease to experimental mouse models of tuberculosis.
© 2018 Moreira-Teixeira et al.
Figures
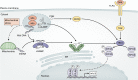
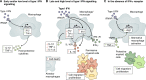
References
-
- Antonelli L.R., Gigliotti Rothfuchs A., Gonçalves R., Roffê E., Cheever A.W., Bafica A., Salazar A.M., Feng C.G., and Sher A.. 2010. Intranasal Poly-IC treatment exacerbates tuberculosis in mice through the pulmonary recruitment of a pathogen-permissive monocyte/macrophage population. J. Clin. Invest. 120:1674–1682. 10.1172/JCI40817 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

