An Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes in a Cohort of Clients on the DOTS Strategy, 2012-2016
- PMID: 29666702
- PMCID: PMC5832068
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4287842
An Evaluation of Treatment Outcomes in a Cohort of Clients on the DOTS Strategy, 2012-2016
Abstract
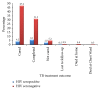
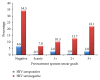
We present, for the first time, an evaluation of treatment outcomes in a cohort at a TB referral centre in the Central Region of Ghana. Of the 213 clients placed on DOTS, 59.2% (126/213) were sputum smear-positive. An overall cure rate of 90.2% (51.6% cured + 37.6% completed) and a death rate of 8.5% (18/213) were estimated. Of the number of clients who died, 5.7% (12/213) were males (χ2 = 2.891, p = 0.699; LR = 3.004, p = 0.699). Deaths were only recorded among clients who were > 19 years old (χ2 = 40.319, p = 0.099; LR = 41.244, p = 0.083). Also, 0.9% (2/213) was lost to follow-up, while 1.4% (3/213) had treatment failure. In total, 13.6% (7.0%, 15/213 males, and 6.6%, 14/213 females) of clients who were placed on DOTS were HIV seropositive. Ages of 40-49 years had the highest number, 13/213 (6.1%), infected with HIV, though the difference among the remaining age groups was not statistically significant (χ2 = 9.621, p = 0.142). Furthermore, 7.0% (15/213) had TB/HIV coinfection. Out of them, 9 were cured and 5 died at home, while 1 had treatment failure. Tuberculosis/HIV infection prevention advocacy and interventions that address sociodemographic determinants of unfavourable treatment outcomes are urgently required to augment national efforts towards control.
Figures
References
-
- Global tuberculosis Control, Surveillance, Planning, Financing- WHO Report 2005: WHO/HTM/TB/2005. Vol. 49. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO; 2005.
-
- Trebueq A., Reider H. L. Two excellent management tools for national tuberculosis programmes; history of prior treatment and sputum status at two months. International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease. 1998;2:184–186. - PubMed
-
- Torman F., editor. Tomans tuberculosis case detection, treatment, and monitoring—questions and answers. 2nd. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organisation; 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

