Cone synapses in mammalian retinal rod bipolar cells
- PMID: 29667170
- PMCID: PMC6031453
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.24456
Cone synapses in mammalian retinal rod bipolar cells
Abstract
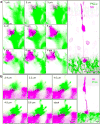
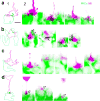
Some mammalian rod bipolar cells (RBCs) can receive excitatory chemical synaptic inputs from both rods and cones (DBCR2 ), but anatomical evidence for mammalian cone-RBC contacts has been sparse. We examined anatomical cone-RBC contacts using neurobiotin (NB) to visualize individual mouse cones and standard immuno-markers to identify RBCs, cone pedicles and synapses in mouse and baboon retinas. Peanut agglutinin (PNA) stained the basal membrane of all cone pedicles, and mouse cones were positive for red/green (R/G)-opsin, whereas baboon cones were positive for calbindin D-28k. All synapses in the outer plexiform layer were labeled for synaptic vesicle protein 2 (SV2) and PSD (postsynaptic density)-95, and those that coincided with PNA resided closest to bipolar cell somas. Cone-RBC synaptic contacts were identified by: (a) RBC dendrites deeply invaginating into the center of cone pedicles (invaginating synapses), (b) RBC dendritic spines intruding into the surface of cone pedicles (superficial synapses), and (c) PKCα immunoreactivity coinciding with synaptic marker SV2, PSD-95, mGluR6, G protein beta 5 or PNA at cone pedicles. One RBC could form 0-1 invaginating and 1-3 superficial contacts with cones. 20.7% and 38.9% of mouse RBCs contacted cones in the peripheral and central retina (p < .05, n = 14 samples), respectively, while 34.4% (peripheral) and 48.5% (central) of cones contacted RBCs (p > .05). In baboon retinas (n = 4 samples), cone-RBC contacts involved 12.2% of RBCs (n = 416 cells) and 22.5% of cones (n = 225 cells). This suggests that rod and cone signals in the ON pathway are integrated in some RBCs before reaching AII amacrine cells.
Keywords: PKCα RRID: AB_477345; Postsynaptic density-95 RRID: AB_10807979; RRID: AB_2313718; RRID: AB_2650488; cone synapse; confocal microscopy; immunohistology; mGluR6 RRID: AB_784501; mouse; primate; rod bipolar cell; synaptic vesicle protein RRID:AB_2315387; tracer injection.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
All authors do not have any known or potential conflict of interest including financial, personal or other relationships with other people or organizations within three years of beginning the submitted work that could inappropriately influence, or be perceived to influence, their work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Rod bipolar cells receive cone photoreceptor inputs through both invaginating synapses and flat contacts in the mouse and guinea pig retinas.J Comp Neurol. 2023 Aug;531(11):1184-1197. doi: 10.1002/cne.25487. Epub 2023 Apr 18. J Comp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 37073449
-
Type 4 OFF cone bipolar cells of the mouse retina express calsenilin and contact cones as well as rods.J Comp Neurol. 2008 Mar 1;507(1):1087-101. doi: 10.1002/cne.21612. J Comp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18095322
-
Rod-cone crossover connectome of mammalian bipolar cells.J Comp Neurol. 2019 Jan 1;527(1):87-116. doi: 10.1002/cne.24084. Epub 2016 Aug 23. J Comp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 27447117 Free PMC article.
-
The neuronal organization of the outer plexiform layer of the primate retina.Int Rev Cytol. 1984;86:285-320. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60181-3. Int Rev Cytol. 1984. PMID: 6368448 Review.
-
Distinct synaptic mechanisms create parallel S-ON and S-OFF color opponent pathways in the primate retina.Vis Neurosci. 2014 Mar;31(2):139-51. doi: 10.1017/S0952523813000230. Epub 2013 Jul 29. Vis Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 23895762 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and maintenance of vision's first synapse.Dev Biol. 2021 Aug;476:218-239. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2021.04.001. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33848537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generators of Pressure-Evoked Currents in Vertebrate Outer Retinal Neurons.Cells. 2021 May 22;10(6):1288. doi: 10.3390/cells10061288. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34067375 Free PMC article.
-
The rod signaling pathway in marsupial retinae.PLoS One. 2018 Aug 29;13(8):e0202089. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0202089. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30157204 Free PMC article.
-
TRPV4 affects visual signals in photoreceptors and rod bipolar cells.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jun 5;18:1404929. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1404929. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38903773 Free PMC article.
-
Diverse Cell Types, Circuits, and Mechanisms for Color Vision in the Vertebrate Retina.Physiol Rev. 2019 Jul 1;99(3):1527-1573. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00027.2018. Physiol Rev. 2019. PMID: 31140374 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aartsen WM, Kantardzhieva A, Klooster J, van Rossum AG, van de Pavert SA, Versteeg I, et al. Mpp4 recruits Psd95 and Veli3 towards the photoreceptor synapse. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006;15:1291–1302. - PubMed
-
- Applebury ML, Antoch MP, Baxter LC, Chun LL, Falk JD, Farhangfar F, et al. The murine cone photoreceptor: a single cone type expresses both S and M opsins with retinal spatial patterning. Neuron. 2000;27:513–523. - PubMed
-
- Bajjalieh SM, Peterson K, Shinghal R, Scheller RH. SV2, a brain synaptic vesicle protein homologous to bacterial transporters. Science. 1992;257:1271–1273. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

