Acute myelogenous leukemia in adolescents and young adults
- PMID: 29667722
- PMCID: PMC6105504
- DOI: 10.1002/pbc.27089
Acute myelogenous leukemia in adolescents and young adults
Abstract
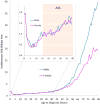
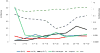
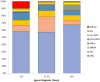
The incidence of acute myelogenous leukemia (AML) increases progressively with age. Favorable genetic mutations are most prevalent in children, and unfavorable profiles increase proportionately in adolescents and young adults (AYA) and into later adulthood. Survival rates of AYA have improved over recent decades to 50-60%, but their accrual to clinical trials remains poor. In contrast to AYA with acute lymphoblastic leukemia, the prognostic benefit for AYA with AML enrolled in pediatric compared with adult trials is minor and only seen when different protocols are used. The distinctive needs of AYA, including intensive psychological services, call for their treatment within specialized centers that offer complex supportive care.
Keywords: acute myelogenous leukemia (AML); adolescents and young adults (AYA); clinical trials; prognosis; survival.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Creutzig U, Buchner T, Sauerland MC, et al. Significance of age in acute myeloid leukemia patients younger than 30 years: a common analysis of the pediatric trials AML-BFM 93/98 and the adult trials AMLCG 92/99 and AMLSG HD93/98A. Cancer. 2008;112:562–571. - PubMed
-
- Kuwatsuka Y, Tomizawa D, Kihara R, et al. Prognostic value of genetic mutations in adolescent and young adults with acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2017 - PubMed
-
- Abrahamsson J, Forestier E, Heldrup J, et al. Response-guided induction therapy in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia with excellent remission rate. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:310–315. - PubMed
-
- Creutzig U, Zimmermann M, Bourquin JP, et al. Randomized trial comparing liposomal daunorubicin with idarubicin as induction for pediatric acute myeloid leukemia: results from Study AML-BFM 2004. Blood. 2013;122:37–43. - PubMed
-
- Gamis AS, Alonzo TA, Meshinchi S, et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin in children and adolescents with de novo acute myeloid leukemia improves event-free survival by reducing relapse risk: results from the randomized phase III Children's Oncology Group trial AAML0531. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32:3021–3032. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

