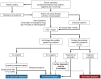
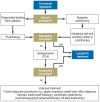
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia
- PMID: 29669681
- PMCID: PMC5938438
- DOI: 10.3238/arztebl.2018.0222
The Diagnosis and Treatment of Functional Dyspepsia
Abstract
Background: Functional dyspepsia (FD) is one of the more common functional disorders, with a prevalence of 10-20%. It affectsthe gastrointestinal tract.
Methods: This article is based on publications retrieved by a selective search of PubMed, with special attention to controlled trials, guidelines, and reviews.
Results: Typical dyspeptic symptoms in functional dyspepsia include epigastric pain, sensations of pressure and fullness, nausea, and early subjective satiety. The etiology of the disorder is heterogeneous and multifactorial. Contributory causes include motility disturbances, visceral hypersensitivity, elevated mucosal permeability, and disturbances of the autonomic and enteric nervous system. There is as yet no causally directed treatment for functional dyspepsia. Its treatment should begin with intensive patient education regarding the benign nature of the disorder and with the establishment of a therapeutic pact for long-term care. Given the absence of a causally directed treatment, drugs to treat functional dyspepsia should be given for no more than 8-12 weeks. Proton-pump inhibitors, phytotherapeutic drugs, and Helicobacter pylori eradication are evidence-based interventions. For intractable cases, tricyclic antidepressants and psychotherapy are further effective treatment options.
Conclusion: The impaired quality of life of patients with functional dyspepsia implies the need for definitive establishment of the diagnosis, followed by symptom-oriented treatment for the duration of the symptomatic interval.
Figures
References
-
- Stanghellini V, Talley NJ, Chan F, et al. Rome IV - Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016 pii: S0016-5085(16)00177-3. - PubMed
-
- Ford AC, Marwaha A, Lim A, Moayyedi P. What is the prevalence of clinically significant endoscopic findings in subjects with dyspepsia? Systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;8:830–837. - PubMed
-
- Madisch A, Hotz J. Gesundheitsökonomische Aspekte der funktionellen Dyspepsie und des Reizdarmsyndroms. Gesundh ökon Qual manag. 2000;5:32–35.
-
- Moayyedi PM, Lacy BE, Andrews CN, Enns RA, Howden CW, Vakil N. ACG and CAG Clinical Guideline: Management of dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112:988–1013. - PubMed
-
- Talley NJ, Ford AC. Functional dyspepsia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1853–1863. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous