Reasons For Physicians Not Adopting Clinical Decision Support Systems: Critical Analysis
- PMID: 29669706
- PMCID: PMC5932331
- DOI: 10.2196/medinform.8912
Reasons For Physicians Not Adopting Clinical Decision Support Systems: Critical Analysis
Abstract
Background: Clinical decision support systems (CDSSs) are an integral component of today's health information technologies. They assist with interpretation, diagnosis, and treatment. A CDSS can be embedded throughout the patient safety continuum providing reminders, recommendations, and alerts to health care providers. Although CDSSs have been shown to reduce medical errors and improve patient outcomes, they have fallen short of their full potential. User acceptance has been identified as one of the potential reasons for this shortfall.
Objective: The purpose of this paper was to conduct a critical review and task analysis of CDSS research and to develop a new framework for CDSS design in order to achieve user acceptance.
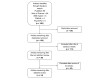
Methods: A critical review of CDSS papers was conducted with a focus on user acceptance. To gain a greater understanding of the problems associated with CDSS acceptance, we conducted a task analysis to identify and describe the goals, user input, system output, knowledge requirements, and constraints from two different perspectives: the machine (ie, the CDSS engine) and the user (ie, the physician).
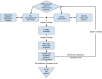
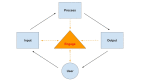
Results: Favorability of CDSSs was based on user acceptance of clinical guidelines, reminders, alerts, and diagnostic suggestions. We propose two models: (1) the user acceptance and system adaptation design model, which includes optimizing CDSS design based on user needs/expectations, and (2) the input-process-output-engagemodel, which reveals to users the processes that govern CDSS outputs.
Conclusions: This research demonstrates that the incorporation of the proposed models will improve user acceptance to support the beneficial effects of CDSSs adoption. Ultimately, if a user does not accept technology, this not only poses a threat to the use of the technology but can also pose a threat to the health and well-being of patients.
Keywords: attitude to computers; decision making, computer-assisted; decision support systems, clinical.
©Saif Khairat, David Marc, William Crosby, Ali Al Sanousi. Originally published in JMIR Medical Informatics (http://medinform.jmir.org), 18.04.2018.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures
References
-
- Patient Safety Network. Patient safety primer: systems approach https://psnet.ahrq.gov/primers/primer/21/systems-approach .
-
- Belard A, Buchman T, Forsberg J, Potter BK, Dente CJ, Kirk A, Elster E. Precision diagnosis: a view of the clinical decision support systems (CDSS) landscape through the lens of critical care. J Clin Monit Comput. 2017 Apr;31(2):261–271. doi: 10.1007/s10877-016-9849-1.10.1007/s10877-016-9849-1 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Castaneda C, Nalley K, Mannion C, Bhattacharyya P, Blake P, Pecora A, Goy A, Suh KS. Clinical decision support systems for improving diagnostic accuracy and achieving precision medicine. J Clin Bioinforma. 2015;5:4. doi: 10.1186/s13336-015-0019-3. https://jclinbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13336-01... 19 - DOI - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Damberg C, Timbie J, Bell D, Hiatt L, Smith A, Schneider E. RAND Corporation. 2012. [2018-02-23]. Developing a framework for establishing clinical decision support meaningful use objectives for clinical specialties https://www.rand.org/pubs/technical_reports/TR1129.html .
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

