Pseudomonas aeruginosa gshA Mutant Is Defective in Biofilm Formation, Swarming, and Pyocyanin Production
- PMID: 29669887
- PMCID: PMC5907650
- DOI: 10.1128/mSphere.00155-18
Pseudomonas aeruginosa gshA Mutant Is Defective in Biofilm Formation, Swarming, and Pyocyanin Production
Abstract
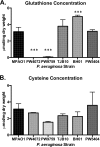
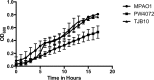
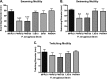
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a ubiquitous Gram-negative bacterium that can cause severe opportunistic infections. The principal redox buffer employed by this organism is glutathione (GSH). To assess the role of GSH in the virulence of P. aeruginosa, a number of analyses were performed using a mutant strain deficient in gshA, which does not produce GSH. The mutant strain exhibited a growth delay in minimal medium compared to the wild-type strain. Furthermore, the gshA mutant was defective in biofilm and persister cell formation and in swimming and swarming motility and produced reduced levels of pyocyanin, a key virulence factor. Finally, the gshA mutant strain demonstrated increased sensitivity to methyl viologen (a redox cycling agent) as well as the thiol-reactive antibiotics fosfomycin and rifampin. Taken together, these data suggest a key role for GSH in the virulence of P. aeruginosaIMPORTANCEPseudomonas aeruginosa is a ubiquitous bacterium that can cause severe opportunistic infections, including many hospital-acquired infections. It is also a major cause of infections in patients with cystic fibrosis. P. aeruginosa is intrinsically resistant to a number of drugs and is capable of forming biofilms that are difficult to eradicate with antibiotics. The number of drug-resistant strains is also increasing, making treatment of P. aeruginosa infections very difficult. Thus, there is an urgent need to understand how P. aeruginosa causes disease in order to find novel ways to treat infections. We show that the principal redox buffer, glutathione (GSH), is involved in intrinsic resistance to the fosfomycin and rifampin antibiotics. We further demonstrate that GSH plays a role in P. aeruginosa disease and infection, since a mutant lacking GSH has less biofilm formation, is less able to swarm, and produces less pyocyanin, a pigment associated with infection.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa; biofilms; glutathione; pyocyanin; thiols; virulence.
Copyright © 2018 Van Laar et al.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa glutathione biosynthesis genes play multiple roles in stress protection, bacterial virulence and biofilm formation.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 16;13(10):e0205815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205815. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30325949 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction of virulence factor pyocyanin production in multidrug-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa.J Infect Chemother. 2013 Feb;19(1):82-8. doi: 10.1007/s10156-012-0457-9. Epub 2012 Aug 3. J Infect Chemother. 2013. PMID: 22865331
-
ZnO nanoparticles inhibit Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence factor production.Microbiol Res. 2014 Dec;169(12):888-96. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2014.05.005. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Microbiol Res. 2014. PMID: 24958247
-
Roles of Two-Component Systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Virulence.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 10;22(22):12152. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212152. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830033 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A biomedical perspective of pyocyanin from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: its applications and challenges.World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Feb 10;40(3):90. doi: 10.1007/s11274-024-03889-0. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38341389 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glutathione Synthesis Regulated by CtrA Protects Ehrlichia chaffeensis From Host Cell Oxidative Stress.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 30;13:846488. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.846488. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35432225 Free PMC article.
-
A Quantitative Survey of Bacterial Persistence in the Presence of Antibiotics: Towards Antipersister Antimicrobial Discovery.Antibiotics (Basel). 2020 Aug 13;9(8):508. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9080508. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32823501 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPRi-Mediated Gene Suppression Reveals Putative Reverse Transcriptase Gene PA0715 to Be a Global Regulator of Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Infect Drug Resist. 2022 Dec 22;15:7577-7599. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S384980. eCollection 2022. Infect Drug Resist. 2022. PMID: 36579125 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa glutathione biosynthesis genes play multiple roles in stress protection, bacterial virulence and biofilm formation.PLoS One. 2018 Oct 16;13(10):e0205815. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0205815. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30325949 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic evaluation and genotypic identification of burn-related Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains isolated from post-burn human infections during hospitalization.Pathog Dis. 2024 Feb 7;82:ftae021. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftae021. Pathog Dis. 2024. PMID: 39496512 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

