Usefulness of the CHADS2 and R2CHADS2 scores for prognostic stratification in patients with coronary artery disease
- PMID: 29670341
- PMCID: PMC5894722
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S156208
Usefulness of the CHADS2 and R2CHADS2 scores for prognostic stratification in patients with coronary artery disease
Abstract
Objective: The current risk model for long-term prediction in coronary artery disease (CAD) is complicated, while a simple useful model is still lacking. We aim to investigate if CHADS2 and R2CHADS2 scores could predict long-term outcome for patients with CAD.
Patients and methods: We enrolled 3,700 patients with CAD between November 2010 and September 2014 at the Department of Cardiology from Chinese PLA General Hospital. The CHADS2 and R2CHADS2 scores were calculated. All cases were followed to track the incidence of composite end point consisting of cardiovascular (CV) death, myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, heart failure, and all-cause death.
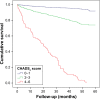
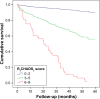
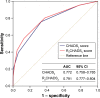
Results: During a median 2.9-year follow-up, 443 patients experienced at least one element of the composite end point of CV death (n=168 [4.6%]), MI (n=59 [1.6%]), stroke (n=96 [2.6%]), heart failure (n=101 [2.8%]), and all-cause death (n=240 [6.6%]). Multivariate Cox regression analyses showed that the CHADS2 score (hazard ratio [HR]: 2.18, 95% CI: 2.00-2.38, p<0.0001) and the R2CHADS2 score (HR: 1.93, 95% CI: 1.83-2.04, p<0.0001) were independently associated with composite outcome. Receiver-operating characteristic analysis showed that compared with the CHADS2 score, the R2CHADS2 score had better discrimination for the prediction of long-term combined outcome (0.772 vs 0.791, p=0.0013).
Conclusion: CHADS2 and R2CHADS2 scores provide a quick and useful tool in predicting long-term outcome for patients with CAD.
Keywords: CHADS2 score; R2CHADS2 score; coronary artery disease; prognosis; renal function; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Townsend N, Wilson L, Bhatnagar P, Wickramasinghe K, Rayner M, Nichols M. Cardiovascular disease in Europe: epidemiological update 2016. Eur Heart J. 2016;37(42):3232–3245. - PubMed
-
- Tang EW, Wong CK, Herbison P. Global registry of acute coronary events (GRACE) hospital discharge risk score accurately predicts long-term mortality post acute coronary syndrome. Am Heart J. 2007;153(1):29–35. - PubMed
-
- Antman EM, Cohen M, Bernink PJ, et al. The TIMI risk score for unstable angina/non-ST elevation MI: a method for prognostication and therapeutic decision making. JAMA. 2000;284(7):835–842. - PubMed
-
- Rietbrock S, Heeley E, Plumb J, van Staa T. Chronic atrial fibrillation: Incidence, prevalence, and prediction of stroke using the Congestive heart failure, Hypertension, Age >75, Diabetes mellitus, and prior Stroke or transient ischemic attack (CHADS2) risk stratification scheme. Am Heart J. 2008;156(1):57–64. - PubMed
-
- Huang SS, Chen YH, Chan WL, Huang PH, Chen JW, Lin SJ. Usefulness of the CHADS2 score for prognostic stratification of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol. 2014;114(9):1309–1314. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

