miR-203 Inhibits Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Targeting Lipin1
- PMID: 29670525
- PMCID: PMC5893905
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00275
miR-203 Inhibits Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Steatosis by Targeting Lipin1
Abstract
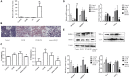
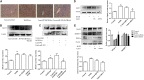
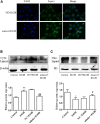
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) is a global liver disease which characterized by liver inflammation, fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, or liver cirrhosis. Alcohol abuse is one of the main reasons for liver disease. Alcoholic fatty liver (AFL) disease is the early stage of ALD and associated with the excessive lipids accumulation in hepatocytes as well as oxidative stress. MicroRNA-203 (miR-203) is known to suppress the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma, but the role in the progression of alcoholic liver disease is not clear and is warranted for further investigation. In the present study, we have found the expression of miR-203 is down-regulated in Gao-Binge alcoholic mice model and ethanol-induced AML-12 cell lines in vitro. Furthermore, over-expression of miR-203 decrease the lipids accumulation in liver and ethanol-induced AML-12 cells. Mechanistically, we identified that Lipin1 is a key regulator of hepatic lipid metabolism, and acts as a downstream target for miR-203. In summary, our results suggested that over-expression of miR-203 inhibited the liver lipids accumulation and the progression of AFL by targeting Lipin1.
Keywords: Gao-binge; Lipin1; alcoholic fatty liver; lipid metabolism; miR-203.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Roles of silent information regulator 1-serine/arginine-rich splicing factor 10-lipin 1 axis in the pathogenesis of alcohol fatty liver disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017 Jun;242(11):1117-1125. doi: 10.1177/1535370217707729. Epub 2017 May 3. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2017. PMID: 28467182 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-708 prevents ethanol-induced hepatic lipid accumulation and inflammatory reaction via direct targeting ZEB1.Life Sci. 2020 Oct 1;258:118147. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118147. Epub 2020 Jul 25. Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 32721464
-
Arrb2 causes hepatic lipid metabolism disorder via AMPK pathway based on metabolomics in alcoholic fatty liver.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 May 28;135(10):1213-1232. doi: 10.1042/CS20201363. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 33871024
-
Hepatic Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor Gamma Signaling Contributes to Alcohol-Induced Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation in Mice.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016 May;40(5):988-99. doi: 10.1111/acer.13049. Epub 2016 Apr 8. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2016. PMID: 27062444 Free PMC article.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
Cited by
-
Integrated Analyses Identify Key Molecules and Reveal the Potential Mechanism of miR-182-5p/FOXO1 Axis in Alcoholic Liver Disease.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Dec 7;8:767584. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.767584. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34950682 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNA and Alcohol Use Disorder: A Scoping Review of Current Research and Knowledge Gaps.Alcohol Res. 2025 Jun 20;45(1):06. doi: 10.35946/arcr.v45.1.06. eCollection 2025. Alcohol Res. 2025. PMID: 40552213 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs in Alcohol-Related Liver Diseases and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward New Therapeutic Approaches?Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 23;15(23):5557. doi: 10.3390/cancers15235557. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38067261 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What are the common downstream molecular events between alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver?Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Feb 8;23(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02031-1. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38331795 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-203 Alleviates Myocardial Damage Caused by Acute Coronary Syndrome by Inhibiting CA125.Biochem Genet. 2025 Feb 28. doi: 10.1007/s10528-025-11069-4. Online ahead of print. Biochem Genet. 2025. PMID: 40019608
References
-
- Barroso E., Rodriguez-Calvo R., Serrano-Marco L., Astudillo A. M., Balsinde J., Palomer X., et al. (2011). The PPARbeta/delta activator GW501516 prevents the down-regulation of AMPK caused by a high-fat diet in liver and amplifies the PGC-1alpha-Lipin 1-PPARalpha pathway leading to increased fatty acid oxidation. Endocrinology 152 1848–1859. 10.1210/en.2010-1468 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

